Ensuring food safety is crucial for protecting public health and maintaining consumer trust. Each year, approximately 600 million people, nearly 1 in 10 worldwide, fall ill after consuming contaminated food each year, leading to 420,000 deaths. In the United States alone, an estimated 48 million people suffer from foodborne illnesses annually, resulting in 3,000 fatalities.
Recent incidents highlight failings in the food safety system. For instance, a listeria outbreak linked to Boar’s Head deli meats led to 10 deaths and numerous hospitalizations, causing a significant decline in cold cut sales.
Similarly, McDonald’s faced an E. coli outbreak traced to contaminated onions, which affected 75 people and resulted in one death. The economic impact of such food safety failures is substantial. Low—and middle-income countries lose an estimated $110 billion annually in productivity and medical expenses due to unsafe food.
In the United States, the financial burden includes costs associated with recalls, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. These incidents serve as an alert in food safety, emphasizing the need for stringent practices. By analyzing past failures and implementing actionable strategies, stakeholders can work towards preventing future occurrences, safeguarding public health, and preserving consumer confidence.
What are Food Safety Failures? – Understanding Food Safety Failures
Food safety failures occur when the processes designed to protect food from contamination break down, posing risks for consumers and businesses. These failures can happen at any point in the food supply chain, from production and processing to storage, transportation, and preparation. By understanding their scope and significance, businesses can better address the challenges they pose and take preventive measures.
Understanding the causes and consequences of food safety failures can help stakeholders develop effective strategies to mitigate risks. From improving hygiene practices to investing in technology for better traceability, the lessons learned from past failings are crucial in creating a safer, more reliable food supply chain.
Definition and Scope
Food safety failures encompass any instance where food becomes contaminated, unsafe, or mislabeled, posing a threat to public health. These can stem from bacterial contamination, chemical hazards, or improper handling. For example, the 2023 nationwide recall of frozen fruit due to listeria contamination affected 23 brands, highlighting failings in the food safety system to identify and address issues early.
The scope of these failures is vast. According to the World Health Organization, unsafe food causes approximately 600 million cases of illness globally each year, with children under five accounting for 40% of foodborne disease cases. In the United States, food safety failures result in annual losses of $15.6 billion, considering medical costs, productivity losses, and food recalls.
Significance
Food safety failures go beyond public health; they erode consumer trust and can cripple businesses financially and reputationally. Companies like Chipotle Mexican Grill, which faced multiple foodborne illness outbreaks between 2015 and 2022, saw stock prices drop and faced hefty fines. Such incidents alert food safety, pushing industries to adopt rigorous food safety practices to prevent future occurrences.
Moreover, these failures disproportionately affect low-income populations and developing countries, where monitoring and enforcing food safety regulations are often inadequate. The economic burden in these regions is estimated to be $110 billion annually. These figures underscore the importance of proactive measures to safeguard food systems globally.
Analysis of Recent Food Safety Incidents & High-Profile Outbreaks
As demonstrated by high-profile food recalls and outbreaks, food safety failures continue to disrupt industries and harm public trust. Analyzing such incidents offers valuable lessons for improving food safety practices, preventing contamination, and protecting consumer health.
Walmart Recall of Broccoli Due to Listeria Concerns
Overview
In 2024, Walmart issued a nationwide recall of pre-packaged broccoli due to concerns about potential listeria contamination. The recall, which impacted thousands of stores across the U.S., highlighted failings in the food safety system, particularly in detecting microbial threats before products reach consumers.
Listeria monocytogenes is a serious foodborne pathogen, especially harmful to pregnant women, newborns, and immunocompromised individuals. While no illnesses were immediately reported, the recall caused widespread concern, raising an alert in food safety about the potential risks of consuming contaminated produce.
The incident eroded consumer trust in pre-packaged vegetables, a previously perceived convenient and safe market. Industry analysts noted a temporary dip in sales of similar products across competitors, reflecting how one incident can ripple across an entire category.
Lessons Learned
The Walmart recall underscores the critical importance of proactive measures to prevent food safety failures:
- Proactive Microbial Monitoring: Regular microbial testing of raw materials and finished products is essential. Early detection of listeria could have prevented contaminated broccoli from entering the supply chain. Companies must invest in advanced testing technologies, such as rapid DNA-based diagnostics, to identify pathogens in real time.
- Supplier Oversight: Effective supplier management is crucial for maintaining food safety practices. Companies must enforce stringent safety standards and regularly audit their suppliers’ facilities to ensure compliance. The recall highlighted the need for transparent communication between suppliers and retailers to address potential risks promptly.
- Consumer Education: The incident also emphasized the importance of educating consumers about proper handling and cooking practices to reduce risks. For example, washing fresh produce thoroughly and following storage instructions can minimize contamination risks.
This recall serves as a sobering reminder of the vulnerabilities in food supply chains. By addressing these failings, companies can strengthen consumer trust and reduce the likelihood of future incidents. The key takeaway is clear: investing in strong monitoring systems and fostering strong supplier partnerships are non-negotiable in today’s food industry.
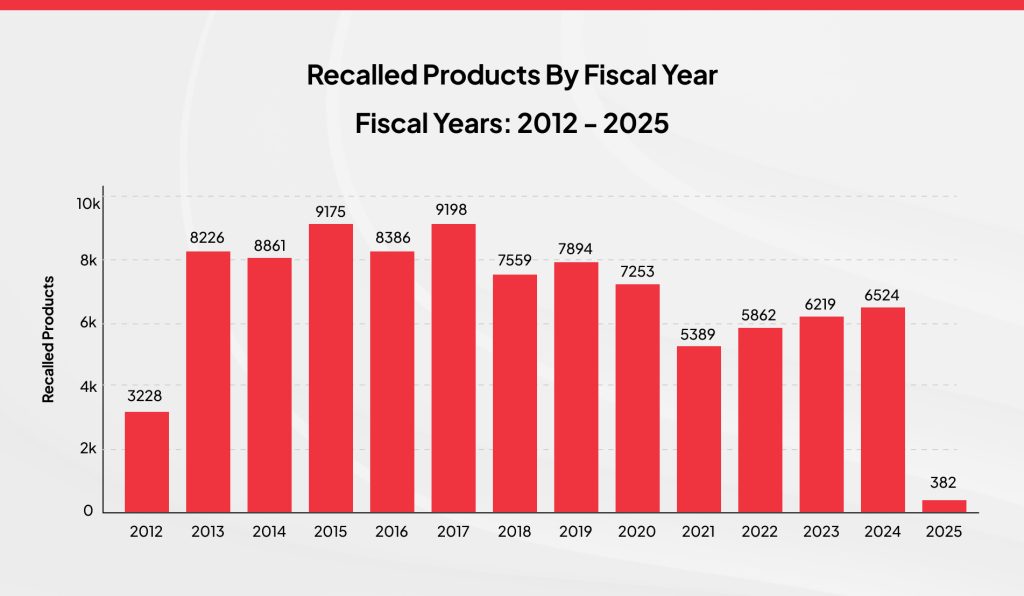
Rise in Food Recalls by 10% in 2024
In 2024, there was a marked 10% increase in food recalls globally, which heightened attention to food safety failures. This alarming trend underscores the critical need for the food industry to address systemic gaps in safety practices and improve response mechanisms.
Overview
Several factors contributed to this rise in food recalls. Stricter regulatory pressures, such as increased enforcement of the FDA’s Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), pushed companies to identify and report risks proactively. Enhanced testing technologies also played a role, enabling faster detection of contaminants like E. coli, salmonella, and listeria in food products.
For instance, the FDA reported a 15% increase in recalls related to undeclared allergens, which remain one of the leading causes of food recalls. Similarly, a listeria outbreak linked to pre-packaged salads affected multiple states, forcing several brands to pull products off the shelves. These incidents highlight failings in the food safety system, emphasizing quality control and oversight gaps.
Beyond regulatory scrutiny, consumer demand for transparency has added pressure on companies to act swiftly during potential crises. Social media amplifies the visibility of recalls, turning isolated incidents into widespread food safety alerts, which can almost instantly damage brand reputations.
Lessons Learned
The rise in recalls reveals critical lessons for food manufacturers and retailers to minimize risks and maintain consumer trust:
- Robust Recall Readiness: Organizations must have a well-defined recall plan to respond swiftly and effectively. This includes maintaining accurate traceability records, training employees on recall protocols, and establishing clear communication channels with regulators and consumers. Proactive recall readiness can significantly reduce the impact of food safety failures.
- Swift Action During Crises: A timely response is crucial when contamination is detected. Companies like Nestlé have set a benchmark by recalling potentially hazardous products within hours of identification. Speed and transparency protect public health and help preserve consumer confidence.
- Enhanced Food Safety Practices: Improved safety measures, such as stricter supplier audits and real-time monitoring systems, can prevent contamination at the source. Combined with routine testing, these practices ensure that hazards are addressed before products reach consumers.
The 10% rise in food recalls is a wake-up call for the industry, urging stakeholders to prioritize safety at every supply chain step. By learning from these incidents and adopting preventive strategies, companies can reduce the likelihood of future recalls, ensuring safer food systems for all.
Cinnamon Applesauce Lead Contamination
Overview
In October 2023, the FDA initiated a public health alert advising parents and caregivers not to purchase or feed WanaBana apple cinnamon fruit puree pouches to children due to elevated lead levels.
Subsequent investigations revealed that the contamination originated from the cinnamon used in these products. Samples collected from the supplier, Negasmart, showed alarmingly high lead concentrations of 5,110 parts per million (ppm) and 2,270 ppm. This incident exposed significant vulnerabilities in the global supply chain and underscored the inadequacy of existing ingredient testing protocols.
Impact
Lead is a potent neurotoxin, and exposure can have severe health consequences, particularly for children. Short-term exposure may cause headaches, abdominal pain, vomiting, and anemia, while long-term exposure can lead to irritability, lethargy, muscle weakness, and developmental delays.
The contamination led to a nationwide recall of affected products, including WanaBana, Schnucks, and Weis brands, disrupting supply chains and eroding consumer trust.
Lessons Learned
- Rigorous Ingredient Testing Protocols: This incident highlights the critical need for comprehensive testing of all ingredients, especially those sourced internationally. Implementing stringent testing measures can detect contaminants like lead before they enter production, preventing food safety failures.
- Supply Chain Transparency and Accountability: Ensuring transparency throughout the supply chain is essential. Companies must establish robust oversight mechanisms and maintain open communication with suppliers to verify compliance with safety standards. Regular audits and certifications can help identify and mitigate ingredient sourcing risks. Contamination incidents serve as a stark alert in food safety, emphasizing the imperative for enhanced food safety practices to protect public health and maintain consumer confidence.
Listeria Monocytogenes Outbreak in Deli Meats
Overview
The outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes linked to deli meats in late 2023 shed light on significant food safety failures. According to the CDC, this outbreak was traced to pre-packaged deli meats sold across multiple states, leading to severe health consequences. Investigations revealed systematic lapses in sanitation practices at processing facilities, including inadequate cleaning protocols and insufficient environmental monitoring. These failures allowed the pathogen to proliferate, posing a significant public health risk.
The incident highlighted failings in the food safety system and emphasized the need for more stringent oversight of high-risk food categories, such as ready-to-eat deli products.
Impact
This outbreak resulted in at least 23 confirmed illnesses, with six fatalities reported. Vulnerable groups, such as older adults, pregnant women, and individuals with weakened immune systems, were disproportionately affected. Listeriosis, caused by Listeria monocytogenes, is a severe infection that can lead to miscarriage, stillbirth, and life-threatening complications in newborns.
The contamination prompted widespread recalls and a loss of consumer trust, as deli meat products from multiple brands were implicated. The economic fallout extended beyond the affected companies, disrupting supply chains and tarnishing the reputation of an entire product category.
Lessons Learned
- Stringent Sanitation Practices: This outbreak underscores the necessity of rigorous sanitation measures in food processing environments. Companies must implement and enforce detailed cleaning protocols to eliminate pathogens like Listeria. Frequent equipment disassembly, cleaning, and staff training are essential to reducing contamination risks.
- Comprehensive Environmental Monitoring Programs: Proactive environmental monitoring is critical in detecting and addressing contamination early. Routine testing of surfaces, equipment, and air quality can help identify hotspots where pathogens may thrive. Companies should establish clear action plans for responding to positive results, ensuring immediate corrective actions to prevent the spread of harmful bacteria.
Cronobacter Sakazakii Contamination in Infant Formula
Overview
In February 2022, the FDA, in collaboration with the CDC, initiated an investigation into reports of Cronobacter sakazakii infections among infants consuming powdered infant formula produced at Abbott Nutrition’s Sturgis, Michigan facility.
Though rare, this pathogen can cause severe and often fatal infections in infants, including sepsis and meningitis. The investigation revealed that the contamination stemmed from lapses in microbial control within the manufacturing environment, highlighting significant food safety failures.
Impact
The contamination led to multiple reported cases of Cronobacter infections, with at least two infants requiring hospitalization. Tragically, one infant succumbed to the disease. In response, Abbott Nutrition voluntarily recalled specific lots of Similac, Alimentum, and EleCare powdered infant formulas. This recall exacerbated an infant formula shortage, causing widespread concern among parents and caregivers and eroding public trust in the safety of essential nutrition products.
Lessons Learned
- Robust Microbial Control Measures: This incident underscores the critical need for stringent microbial control protocols in infant formula production. Manufacturers must implement comprehensive environmental monitoring programs to promptly detect and address potential contaminants. Regular testing of raw materials, in-process samples, and finished products is essential to prevent contamination and ensure product safety.
- Effective Crisis Communication: Maintaining public trust during product recalls and shortages necessitates transparent and timely communication. Companies should proactively inform consumers about potential risks, recall specifics, and alternative options. Collaborating with health authorities to disseminate accurate information can help mitigate panic and maintain confidence in the food safety system.
Manage Food Safety Without the Paper Trail
Transition from paper-based systems to a digital solution that helps you manage
HACCP plans, monitor critical control points, and stay compliant with FDA/FSMA regulations.
Talk To a Food Safety Specialist
Impacts of Food Safety Failures on Businesses
Food safety failures affect public health and can have far-reaching consequences for businesses. From tarnished reputations to financial losses, the repercussions underscore why food safety practices are critical to every company in the industry.
Brand Reputation
A single food recall can severely damage consumer trust, as customers lose confidence in a brand’s ability to prioritize safety. According to a 2024 consumer survey by the Food Marketing Institute, 67% of respondents indicated they would avoid purchasing products from a brand associated with a major food safety incident. This highlights failings in the food safety system and underscores the long-lasting impact of negative publicity. Rebuilding trust often requires years of effort, extensive marketing campaigns, and stringent operational reforms.
Financial Losses
The financial fallout from food safety failures can be devastating. Businesses face lost revenue due to halted production, fines from regulatory bodies, and legal settlements stemming from consumer lawsuits. For instance, the Listeria outbreak linked to deli meats in 2023 cost companies over $180 million in recalls, legal fees, and lost sales. The strain is even greater for smaller businesses, which may not recover from such financial blows.
Operational Disruptions
Recalls demand immediate action, diverting resources from routine operations to crisis management. The logistical burden, from tracing affected batches to managing customer inquiries, can paralyze day-to-day activities. In the aftermath, businesses often need to overhaul food safety practices, which requires additional time, training, and investment.
Regulatory Backlash
Non-compliance with food safety standards invites scrutiny and penalties from regulatory authorities. Businesses found guilty of negligence may face license suspensions, increased inspections, and additional compliance requirements. Moreover, a poor safety record can disqualify companies from lucrative contracts or partnerships, as buyers demand accountability and transparency.
How Can These Lessons Be Transformed Into Actionable Strategies?
Preventing food safety failures requires turning hard-earned lessons into proactive strategies. Businesses can minimize risks and protect public health by strengthening supplier management and enhancing sanitation and environmental monitoring. Food Safety Management Platforms (FSMPs) can significantly organize these efforts by centralizing all food safety activities in one system, enhancing overall efficiency and compliance.
Strengthening Supplier Management
Effective supplier management is crucial for preventing food safety failures, as many issues originate from raw materials and external vendors. Food Safety Management Platforms (FSMPs) play an essential role in tracking supplier compliance and certifications and facilitating smooth recall management.
1. Establish Robust Verification Processes
Ensuring that suppliers meet stringent safety standards is critical. Implementing a comprehensive framework for evaluating and approving suppliers can reduce risks. This should include:
- Initial audits to assess safety protocols.
- Historical compliance reviews to evaluate past performance.
- Certifications like GFSI (Global Food Safety Initiative) to confirm adherence to global standards.
Food safety platforms centralize these processes, making storing and retrieving verification data and compliance records easier. According to a 2023 study, businesses that adopted FSMPs saw a 35% improvement in supplier verification efficiency.
2. Continuous Monitoring and Communication
Real-time tracking systems powered by FSMPs help businesses monitor supplier performance continuously. Food safety software, for example, enables businesses to track compliance and certifications in real time, ensuring quick responses to alerts about food safety practices. Digital platforms can facilitate open communication between companies and suppliers, allowing for a collaborative approach to managing potential risks.
3. Risk-Based Supplier Audits
Prioritize resources by focusing audits on high-risk suppliers or regions. Businesses can effectively manage and mitigate risk by automating supplier documentation and audit tracking with FSMPs. This approach can highlight failings in the food safety system, guiding businesses to allocate resources where they’re most needed. With food safety software, supplier audits are organized, reducing time and errors in manual processes.
4. Traceability Across the Supply Chain
Technology solutions like blockchain and FSMPs can track raw materials from their origin to production. These tools help centralize the recall process, allowing businesses to act swiftly in case of contamination. In 2024, 62% of companies with robust traceability systems reduced recall times by over 30%. Using food safety software, businesses can ensure their supply chains are equipped for fast response, directly integrating recall readiness into supply chain management.
Implementing Robust Sanitation and Environmental Monitoring
Sanitation and environmental monitoring are foundational to preventing food safety incidents, and FSMPs are key to organizing these practices.
1. Compliance with Regulatory Bodies
Meeting FDA, USDA, and global standards ensure businesses stay ahead of regulatory expectations. FSMPs offer paperless checklists, audits, and HACCP compliance solutions, reducing human error and improving the speed of audits. Companies using digital tools have reported a 40% improvement in sanitation oversight and compliance tracking.
2. Establishing Effective Crisis Management and Communication Plans
Food safety failures demand a rapid, coordinated response. A well-structured crisis management plan should include:
- Immediate identification and isolation of the issue.
- Transparent communication with the public to preserve trust.
With FSMPs, recall management can be fully integrated, enabling businesses to quickly identify affected products and notify consumers. For example, food safety software can centralize recall efforts, automate alerts, and track responses, ensuring a swift and transparent crisis resolution.
This kind of integrated system is vital for maintaining trust during food safety failures, such as the 2022 Cronobacter Sakazakii outbreak in infant formula, where delayed communication resulted in a loss of public confidence.
Conclusion
Food safety failures can have devastating consequences for public health, businesses, and consumer trust. Understanding these failures and implementing actionable strategies can help companies prevent future incidents and improve their food safety practices.
Strengthening supplier management, enhancing sanitation and environmental monitoring, and using advanced Food Safety Management Platforms (FSMPs) offer businesses a powerful way to centralize food safety efforts, organize compliance, and respond swiftly to crises.
Adopting these strategies helps businesses minimize risks, ensure they are better prepared for recalls, and maintain public trust through transparent communication and timely action. Food safety is an ongoing commitment, and businesses that prioritize proactive measures will be better equipped to avoid costly and harmful mistakes.
Once you transform lessons learned into structured, effective action plans, companies can safeguard their reputation, ensure compliance, and ultimately protect public health.
Manage Food Safety Without the Paper Trail
Transition from paper-based systems to a digital solution that helps you manage
HACCP plans, monitor critical control points, and stay compliant with FDA/FSMA regulations.
Talk To a Food Safety Specialist
FAQs
What Are The Most Common Causes Of Food Safety Failures?
Food safety failures often stem from inadequate supplier management, poor sanitation practices, and lack of proper environmental monitoring. Issues such as improper storage, cross-contamination, and insufficient testing also contribute to food safety risks.
How Can Food Safety Management Platforms (FSMPs) Help Businesses Prevent Food Safety Failures?
FSMPs help businesses track supplier compliance, certifications, and certifications in real time, ensuring adherence to food safety standards. These platforms also centralize recall management, providing businesses with the tools needed for rapid response during crises.
How Can Supplier Management Be Improved To Prevent Food Safety Failures?
Businesses can ensure that suppliers meet safety standards by implementing a robust verification process, conducting regular audits, and tracking supplier performance through digital platforms. Real-time monitoring and risk-based audits are essential for managing high-risk suppliers.
What Is The Role Of Sanitation And Environmental Monitoring In Preventing Food Safety Failures?
Strict sanitation practices and environmental monitoring programs are critical to prevent contamination. Regular audits and real-time tracking of hygiene practices can help identify potential risks early, reducing the chances of an outbreak.
How Do Food Recalls Affect Businesses?
Food recalls can significantly damage a company’s reputation, lead to financial losses through fines, legal settlements, and lost revenue, and cause operational disruptions. Prompt, effective crisis management and communication are essential to minimize these impacts and restore consumer trust.
Why Is Traceability Across The Supply Chain Important For Food Safety?
Traceability ensures that raw materials can be tracked from their source to the final product. This system is crucial for quickly identifying and isolating contaminated products during a recall, minimizing the impact of food safety failures.
How Can Businesses Improve Crisis Management During Food Safety Incidents?
Establishing clear crisis management plans, maintaining open communication channels, and implementing technology solutions for swift recall management are key to effective crisis resolution. Transparent communication with consumers is essential to preserve trust.