Efficiency, accuracy, and seamless coordination are the pillars of success for any business. Yet, managing multiple departments, from finance to supply chain, can quickly become overwhelming without the right tools. This is where Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems come in.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become indispensable tools for achieving these objectives. ERP software integrates various business processes, such as procurement, production, distribution, and finance, into a unified system, enhancing operational efficiency and data accuracy.
But what is ERP? ERP software is Enterprise Resource Planning, a technology designed to integrate and streamline business operations into a single, centralized system. By automating processes, reducing manual errors, and enhancing data visibility, ERP helps businesses make smarter decisions and improve overall efficiency.
The impact of ERP is undeniable. The global ERP market, valued at $54.76 billion in 2022, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.4%, reaching $123.41 billion by 2030. Additionally, research shows that 95% of businesses experience operational improvements after implementing an ERP system, making it a game-changer across industries.
So, how does ERP work, and why is it essential for modern businesses? This guide will explore the meaning of ERP systems, their core functions, and how they drive growth in today’s competitive market.
What Is ERP?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a comprehensive software system that manages and integrates a company’s core business functions within a centralized platform. By unifying finance, procurement, inventory, supply chain, human resources, and customer relationship management, ERP eliminates data silos and enhances collaboration across departments.
Businesses of all sizes use ERP to improve efficiency, data accuracy, and decision-making. Unlike standalone software that handles only specific tasks, ERP consolidates real-time data into a single source of truth, enabling organizations to optimize their operations and remain competitive.
ERP Systems Definition
ERP systems enable businesses to automate and optimize workflows by providing real-time data visibility and centralized control over various departments. Unlike standalone software solutions that cater to specific functions, ERP consolidates all aspects of business operations, ensuring seamless collaboration and data accuracy across the organization.
ERP Software Stands For
ERP software stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. It encompasses integrated applications that help businesses manage daily operations efficiently. These systems are tailored to meet the unique challenges of different industries.
Historical Evolution of ERP Systems
The concept of ERP has evolved significantly over the decades, adapting to the growing complexities of modern business operations. The meaning of ERP systems has evolved significantly over time, adapting to changing business needs:
- 1960s – MRP (Material Requirements Planning): Early ERP solutions focused on inventory control and production planning in manufacturing.
- 1980s – MRP II (Manufacturing Resource Planning): Expanded to include capacity planning and financial tracking.
- 1990s – ERP Emerges: Businesses began integrating finance, HR, and supply chain management into a unified system. Major ERP providers like SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft gained prominence.
- 2000s – Cloud-Based ERP: Cloud computing revolutionized ERP, making systems accessible from anywhere while reducing IT infrastructure costs.
- Today – AI-Driven & Industry-Specific ERP: Modern ERP platforms use artificial intelligence, machine learning, and predictive analytics to enhance automation and decision-making.
Core Components and Functionalities of ERP
ERP systems integrate multiple business functions into a centralized platform. Below are the core components and their functionalities:
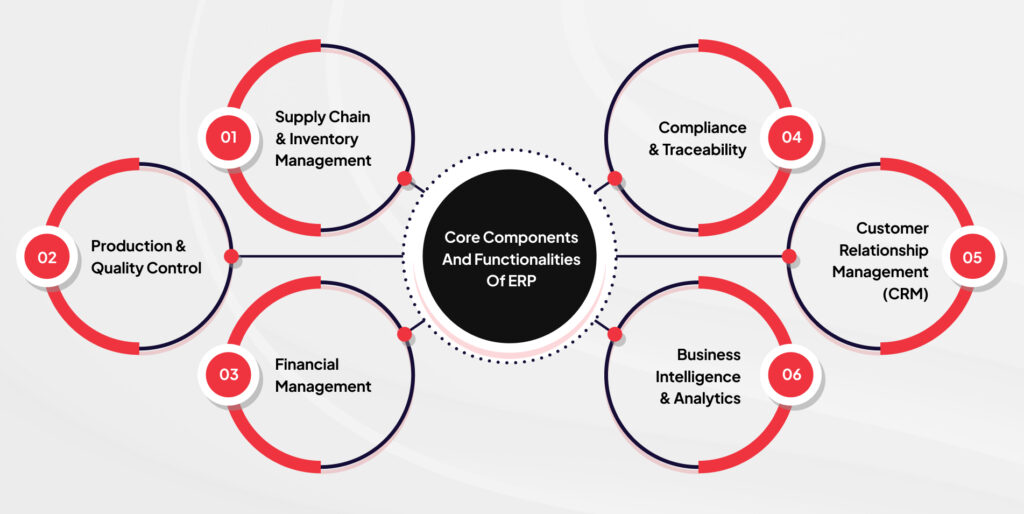
Supply Chain & Inventory Management
- Tracks raw materials, production, and finished goods.
- Optimizes procurement and reduces wastage.
- Ensures real-time visibility into stock levels and supply chain logistics.
Production & Quality Control
- Manages manufacturing schedules and automates workflows.
- Ensures compliance with food safety regulations (e.g., FDA, FSMA).
- Facilitates real-time monitoring of production lines and quality checks.
Financial Management
- Provides real-time financial reporting and budgeting tools.
- Automates billing, accounts payable, and receivable.
- Ensures cost tracking and profit margin optimization.
Compliance & Traceability
- Enables lot tracking and ingredient traceability from farm to fork.
- Helps in quick recall management and regulatory reporting.
- Ensures adherence to industry standards like SQF, BRC, and HACCP.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Enhances customer interactions and sales forecasting.
- Manages order tracking and personalized customer support.
- Helps in demand planning and market trend analysis.
Business Intelligence & Analytics
- Provides actionable insights through real-time dashboards.
- Uses AI and machine learning to forecast demand and optimize operations.
- Helps manufacturers make data-driven decisions to improve efficiency.
How Does ERP Work?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are pivotal in unifying various organizational business processes. Understanding how ERP works involves examining its integration capabilities, centralized data management, real-time processing, and specific departmental workflows.
Integration of Various Business Processes
ERP systems integrate multiple business functions—procurement, production, quality control, inventory management, and finance—into a cohesive platform. This integration ensures data flows effortlessly between departments, reducing manual interventions and minimizing errors. For instance, when a sales order is received, the ERP system automatically updates inventory levels, schedules production, and generates financial records, ensuring all departments are synchronized. This level of coordination plays a key role in optimizing small business operations by improving transparency, accelerating workflows, and supporting better decision-making.
Centralized Data Management and Its Benefits
Centralized data management is a cornerstone of ERP systems. By consolidating data into a single repository, ERP provides a unified source of truth accessible to all authorized users. This centralization offers several benefits:
- Improved Decision-Making: Access to consistent and accurate data enables informed decision-making across the organization.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Departments can collaborate more effectively, accessing the same information and insights.
- Regulatory Compliance: Centralized records simplify adherence to industry regulations and standards, which are crucial.
Real-Time Data Processing and Analytics
Modern ERP systems process data in real time, providing immediate insights into various operations. This capability is vital for:
- Monitoring Production Efficiency: Real-time data helps track production metrics, identify bottlenecks, and optimize processes.
- Ensuring Quality Control: Instant access to quality data allows for swift responses to deviations, maintaining product standards.
- Managing Supply Chains: Real-time analytics facilitate better demand forecasting and inventory management, reducing waste and ensuring timely deliveries.
Examples of ERP Workflows in Different Departments
ERP systems organize various departmental workflows. Here are examples:
Sales Order Processing
- Order Receipt: The Sales team inputs customer orders into the ERP system.
- Inventory Check: The System verifies product availability.
- Production Scheduling: If stock is insufficient, ERP schedules manufacturing.
- Order Fulfillment: Coordinates packaging and shipping.
- Invoicing: Generates and sends invoices to customers.
Purchase Order Approval
- Request Submission: The Department submits the purchase request.
- Approval Workflow: ERP routes request to appropriate manager.
- Order Placement: The system sends a purchase order to the supplier upon approval.
- Receiving Goods: Updates inventory upon receipt.
- Payment Processing: Manages supplier payments.
Inventory Management
- Stock Monitoring: Continuously tracks inventory levels.
- Reorder Alerts: Notifies when stock falls below thresholds.
- Waste Reduction: Identifies slow-moving items to minimize spoilage.
- Compliance Tracking: Ensures storage conditions meet regulatory standards.
Why Does The Food Industry Need A Specialized ERP?
The food industry faces unique challenges that generic ERP systems often fail to address. From stringent regulatory compliance to perishable inventory management, businesses in this sector require specialized ERP solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance and Food Safety
Food manufacturers must comply with strict industry regulations such as FDA, USDA, HACCP, and FSMA. A specialized food ERP system includes built-in compliance management tools, helping businesses track safety protocols, maintain audit trails, and ensure quality control at every production stage.
Managing Perishable Inventory and Supply Chain Efficiency
Unlike other industries, food businesses deal with expiration dates, batch tracking, and temperature-sensitive storage. A food ERP provides real-time inventory monitoring, automated alerts for expiring products, and optimized supply chain management to reduce waste and ensure freshness.
Recipe and Formula Management
Food production requires precise ingredient tracking, batch scaling, and cost analysis. A specialized ERP system integrates recipe management, allowing businesses to maintain consistency, comply with nutritional labeling requirements, and adjust formulations based on demand and regulations.
Handling Seasonal Demand and Production Scalability
The food industry experiences fluctuations in demand due to seasonality, holidays, and market trends. A food ERP system provides advanced forecasting tools, production scheduling, and scalability features to handle high-volume operations efficiently.
Traceability and Recall Management
In a product recall, businesses must act swiftly to identify and remove affected batches from the market. A specialized ERP system enables end-to-end traceability, helping companies track raw materials, finished goods, and distribution channels for quick and efficient recall management.
How to Select the Best Food ERP for Your Business?
Choosing the right Food ERP system is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and long-term growth. With numerous ERP solutions available, businesses must evaluate their options carefully to select a system that aligns with their unique needs. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Identify Your Business Requirements
Before selecting an ERP, conduct an internal assessment to determine your core operational needs. Consider aspects such as:
- Regulatory Compliance (FDA, USDA, FSMA, HACCP)
- Lot & Batch Traceability for recall management
- Inventory & Expiry Date Tracking to manage perishable goods
- Production Planning & Recipe Management for maintaining product consistency
- Supply Chain Optimization to reduce costs and streamline logistics
2. Choose Between Cloud-Based or On-Premise ERP
ERP systems are available in cloud-based and on-premise models:
- Cloud-based ERP offers flexibility, scalability, and lower upfront costs. It’s ideal for businesses with real-time data access, remote monitoring, and automatic updates.
- On-premise ERP provides greater control over data and system customization but requires significant IT infrastructure and maintenance.
3. Evaluate Industry-Specific Features
A generic ERP may not fully support the unique needs of food manufacturers. Look for an ERP with features tailored to the food industry, such as:
- Food Safety & Quality Control to ensure compliance with safety regulations
- Shelf-life & Expiry Management to minimize waste
- Recipe & Formula Management for accurate ingredient usage
- Supply Chain & Warehouse Management to optimize logistics
4. Assess Integration Capabilities
A Food ERP should integrate seamlessly with existing business tools, including:
- Accounting software (e.g., QuickBooks, NetSuite)
- Supply chain management platforms
- E-commerce & customer relationship management (CRM) systems
- IoT-enabled devices for real-time production monitoring
5. Ensure User-Friendliness & Scalability
An ERP system with an intuitive interface and role-based access controls should be easy to use. Additionally, choose a system that can scale with your business growth, whether you expand production, add new distribution channels, or enter new markets.
6. Compare Costs & ROI
While ERP implementation requires an investment, the long-term benefits outweigh the costs. Consider:
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) – including licensing, implementation, training, and support.
- Return on Investment (ROI) – improved efficiency, reduced waste, and enhanced decision-making.
7. Select a Reliable ERP Vendor
Choose an ERP provider with experience in the food industry. Evaluate:
- Customization & Flexibility to adapt to unique business needs
- Reputation & Industry Expertise
- Customer Support & Training Services
Folio3 FoodTech – The Best Industry-Specific ERP for Food Manufacturers
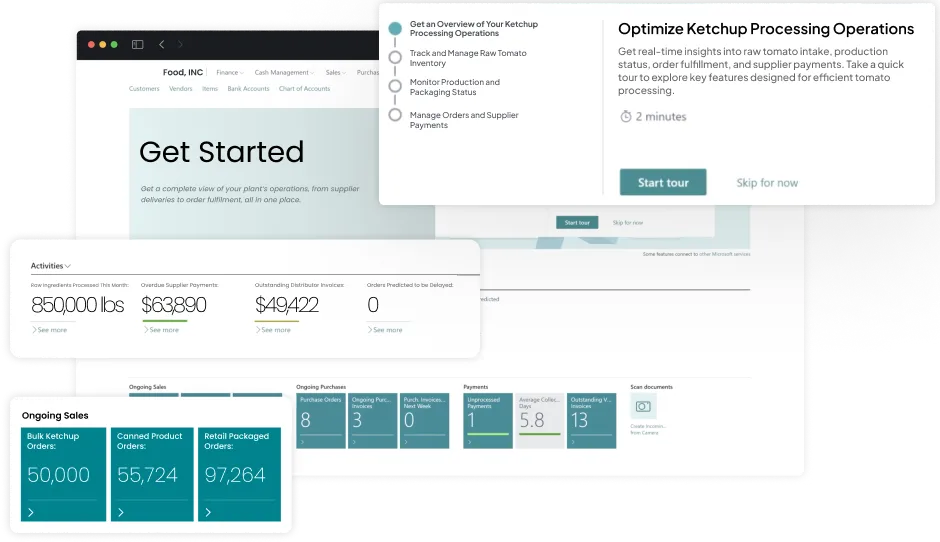
Folio3 FoodTech offers a comprehensive suite of industry-specific food and beverage ERP solutions tailored to meet the unique challenges of food manufacturers. Their platform integrates various business processes, ensuring compliance, enhancing efficiency, and maintaining product quality across multiple sectors within the food industry.
Key Industry-Specific ERP Solutions by Folio3 FoodTech:
- Food & Beverage ERP: Organizes operations, ensures food safety compliance, and optimizes the supply chain for food and beverage companies.
- Bakery ERP: Manages recipe formulations, tracks ingredient costs, and maintains consistent product quality for bakery operations.
- Dairy ERP: Enhances milk yield, minimizes waste. ERP in the dairy industry ensures compliance with the dairy industry regulations.
- Confectionery ERP: Addresses the unique challenges of confectionery manufacturers, including quality control and production efficiency.
- Frozen Food ERP: Optimizes inventory management, ensures traceability, and maintains product quality in the frozen food sector.
- Meat ERP: Provides complete process visibility from slaughter to packaging, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
- Snacks ERP: Manages recipes, tracks allergens, ensures compliance, and simplifies production to maintain quality and boost operational efficiency.
- Sauces & Dressings ERP: Reduces costs and waste, manages shelf life, and ensures food safety for sauces and dressings manufacturers.
Conclusion
ERP solutions seamlessly integrate business processes, provide real-time data insights, and improve decision-making. They help companies enhance efficiency, reduce operational costs, and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Understanding ERP and its workings allows businesses to choose the right system that aligns with their growth objectives and industry needs. Whether you want to streamline supply chain operations, optimize financial management, or improve customer relations, an ERP system can drive productivity and long-term success.
For businesses seeking a tailored ERP solution, Folio3FoodTech offers customized ERP implementations designed to optimize workflows, ensure compliance, and scale with your evolving business needs.
Contact Folio3 FoodTech today to explore how an ERP system can transform your organization and unlock new growth opportunities.
FAQs
What Is An ERP System, & How Does It Work?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a software system that integrates and manages core business processes like finance, supply chain, and production through a centralized platform.
What Is An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) & What Is Its Purpose?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) integrates various business functions into a unified system to organize operations, enhance data accuracy, and improve efficiency.
What Is The Best Definition Of Enterprise Resource Planning Or ERP?
ERP is a business management software that centralizes data, automates processes, and facilitates real-time organizational decision-making.
What Are The 5 Components Of ERP?
ERP’s key components include Finance and accounting, Human Resources, Supply Chain Management, Manufacturing, and Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
What Are The 5 Pillars Of ERP?
The five pillars of ERP are Integration, Automation, Data Analysis, Reporting, and Customer Relationship Management.
What Is An ERP Software Example?
SAP, Oracle NetSuite, and Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Food and Beverage are widely used ERP systems that help businesses organize operations.
What Is The Difference Between CRM & ERP?
ERP manages internal business processes like finance and supply chain, while CRM focuses on customer interactions and sales management.
What Is The Function Of ERP?
ERP enhances business efficiency by centralizing data, automating workflows, and improving department decision-making.
What Are The Three Common Types Of ERP?
The three main types of ERP are On-Premises, Cloud-Based, and Hybrid, each offering different levels of control and scalability.
How Does A Food ERP Help With Food Safety & Recall Management?
A Food ERP system provides real-time lot and batch traceability, allowing businesses to track ingredients from suppliers to final products.