Over 220 million people worldwide suffer from food allergies, and a single misstep in manufacturing can trigger severe — sometimes fatal — allergic reactions. The World Allergy Organization reports a steady rise in food allergy cases, especially among children, with hospital admissions for anaphylaxis increasing by over 300% in the past decade. This isn’t just a health risk for food manufacturers — it’s a major compliance and brand reputation concern.
Food allergen management is no longer a box to check — it’s a critical responsibility that demands structured policies, real-time oversight, and cross-functional coordination. From incorrect labeling to cross-contact during production, the consequences of poor allergen control management can lead to food recalls, legal action, and loss of consumer trust.
Regulatory bodies like the FDA and FSA are tightening expectations, urging companies to adopt a strong allergen management policy that safeguards consumers and the integrity of the supply chain. Whether you’re a seasoned food safety consultant, a regulatory compliance expert, or part of a food production team, implementing a well-documented plan is no longer optional.
Let’s explore the best practices for allergen management in the food industry, how to build an airtight framework that aligns with safety expectations and industry regulations, and why proactive planning could be your strongest asset.
Understanding Food Allergens – What Manufacturers Need to Know
Food allergens are not just a consumer health concern—they’re a manufacturing risk that requires proactive planning and control. For food producers, understanding what allergens are, how they behave in processing environments, and where risks occur is the first step toward building an effective strategy for allergens.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recognizes nine major food allergens: milk, eggs, peanuts, tree nuts, wheat, soy, fish, shellfish, and sesame (added in 2023). These allergens are responsible for the vast majority of allergic reactions in consumers. Even trace amounts left on shared equipment or unintentionally included in a product can trigger serious health consequences.
The Rising Risk – Why Allergen Control Is Critical?
In 2022, the Food Safety Authority of Ireland reported that food safety failures due to undeclared allergens rose by 33% compared to the previous year, highlighting the ongoing need for stronger allergen control practices. For manufacturers, this means identifying all potential allergen risks throughout the supply chain, starting with ingredients and continuing through storage, production, and packaging.
Using Technology for Traceability and Labeling
Many manufacturers are increasingly adopting software solutions to manage allergens and ensure effective compliance with food safety regulations. These advanced tools enable companies to efficiently track raw material sources, manage equipment changeovers, and automate allergen labeling, critical components of accurate product information for consumers.
Additionally, digital record-keeping simplifies the auditing process and facilitates the quick detection and correction of errors. By integrating these solutions, manufacturers can enhance their allergen management practices, reduce the risk of mislabeling, and streamline overall food safety operations.
Tailoring Allergen Control to Your Production Needs
Every facility has unique challenges. An effective allergen management plan must reflect your product lines, processing steps, and risk areas. Manufacturers can reduce cross-contact risk by implementing specific food allergen management practices, such as dedicated lines for allergen-containing products or validated cleaning procedures.
Setting the Standard in Allergen Management
Effective management of allergens in food manufacture and production is about more than just compliance. It’s about protecting consumers, preventing costly food recalls, and upholding your brand’s integrity. By combining clear policies, the right tools, and a commitment to best practices, manufacturers can strengthen their approach to food allergen management to meet today’s standards and adapt to tomorrow’s challenges.
Common Challenges in Allergen Management for Food Manufacturers
While managing allergens is a critical responsibility in food manufacturing, it comes with various challenges. Even the most diligent manufacturers can face obstacles when implementing effective allergen control practices. Here are some of the most common challenges food manufacturers encounter:
Cross-Contamination Risks
One of the most significant risks in allergen management is cross-contamination. Even a tiny amount of an undeclared allergen can have severe health consequences for sensitive individuals. A 2023 study by the Food Allergy Research and Education (FARE) group found that cross-contact during manufacturing was a leading cause of allergic reactions to food products. For example, shared equipment, improper cleaning practices, or poorly maintained production lines can all result in cross-contamination between products containing allergens and those that do not.
Many manufacturers are adopting stricter management of allergen control measures, including designated production lines, dedicated cleaning tools, and thorough sanitation protocols to address this. However, maintaining these standards requires continuous monitoring and regular audits to ensure no allergen traces are left behind.
Labeling Errors
Accurate allergen labeling is not just a legal requirement but a matter of consumer safety. It typically arises from human error, department miscommunication, or inaccurate data entry into product labels.
Allergen labeling errors can have significant consequences, not just for consumer health but also for a company’s reputation and legal standing. Manufacturers can reduce this risk by implementing an allergen software solution that automates and tracks labeling data, ensuring that the final product label is accurate and up to date with any ingredient or formulation changes.
Supply Chain Complexity
With global sourcing and an ever-expanding list of suppliers, managing allergens in the supply chain has become more complex. Supply chain management is a major concern, as manufacturers rely on ingredient suppliers to provide accurate allergen information. Inconsistent labeling practices, inadequate documentation, or a lack of supplier communication can introduce allergens into the production process without proper oversight.
More than 40% of food safety incidents were linked to supply chain issues, particularly undeclared allergens. To combat this, manufacturers must establish strong relationships with suppliers and incorporate specific food allergen protocols, including detailed verification processes, regular audits, and stringent supplier audits for food traceability.
Employee Training Gaps
Employee training is essential in any manufacturing process. To manage allergens, staff must understand the importance of avoiding cross-contact, the risks of mislabeling, and how to follow allergen-specific cleaning procedures. Gaps in employee training are a recurring challenge, especially in environments with high turnover rates or when new staff are introduced.
Nearly 20% of allergen-related incidents can be traced back to a lack of proper training or failure to follow allergen safety protocols. To address this, manufacturers must incorporate comprehensive, ongoing training programs into their plans. This training should focus on general allergen awareness, the specific allergens used in the facility, and the company’s internal management procedures.
Changing Regulations and Compliance Standards
Food allergen regulations continue to evolve, requiring manufacturers to stay up-to-date with the latest guidelines. For example, in 2023, the FDA’s Food Allergen Labeling and Consumer Protection Act (FALCPA) expanded the definition of “major allergens” to include sesame, adding a new layer of compliance for manufacturers. Keeping up with changing regulations requires vigilance and the ability to adapt to new requirements quickly.
The introduction of software can help manufacturers stay ahead of regulatory changes by providing real-time updates on new requirements and facilitating faster, more accurate documentation and compliance reporting.
Lack of Standardized Practices
While there are industry guidelines for allergen management, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. Each facility must customize its management of allergens in food manufacture and production based on its specific risks, products, and production environments. This can make it challenging for food manufacturers to standardize processes across locations, especially for those with multiple production lines or diverse product offerings.
To overcome this, food manufacturers should develop a flexible policy tailored to different products and production conditions while maintaining consistency in core allergen control procedures.
Fix the Gaps in Your Operations
with an ERP That Speaks Food
We help food businesses move from generic or patchworked systems to a fully
integrated ERP, purpose-built for the industry, and designed for you.
Talk to Our Food ERP Specialist
Best Practices for Allergen Management in the Food Industry
Effective management of allergens is essential for ensuring consumer safety and maintaining compliance in the food industry. Implementing robust allergen control practices helps reduce the risk of cross-contamination, improve product consistency, and avoid costly recalls. Below are the best practices that food manufacturers can adopt to ensure better food allergen management.
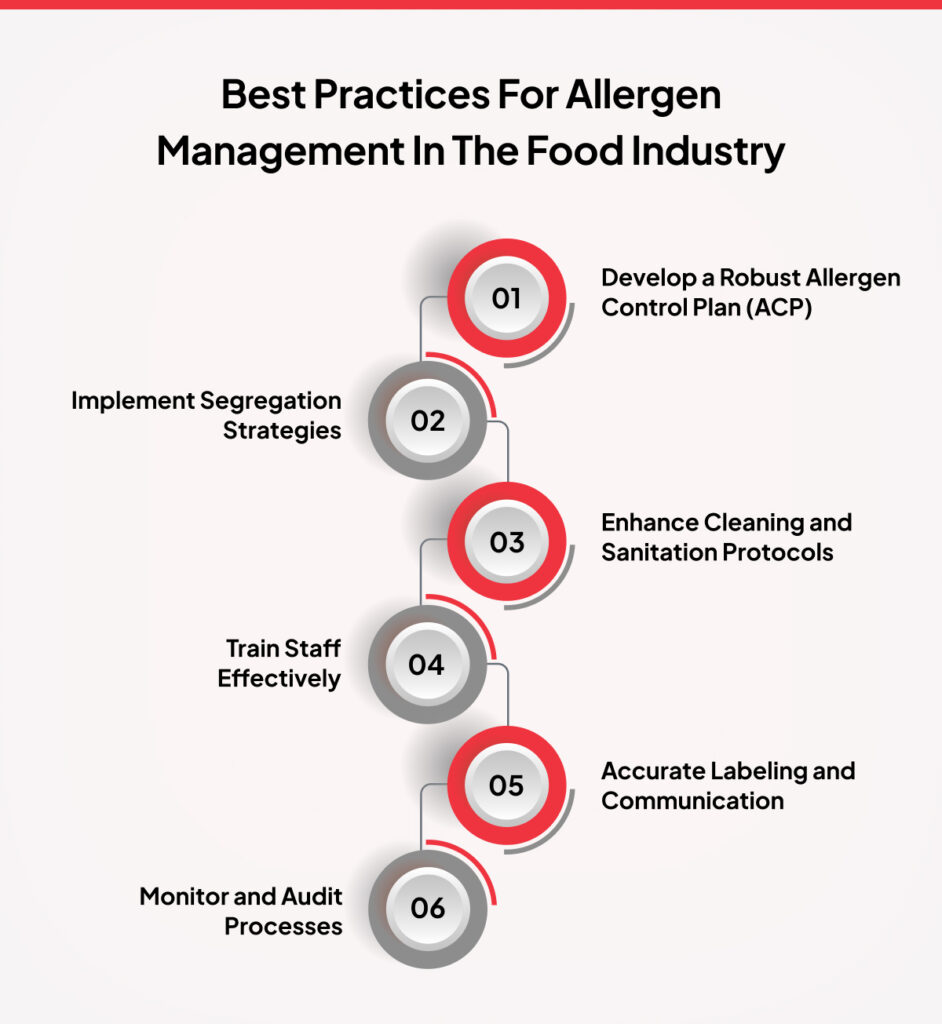
1. Develop a Robust Allergen Control Plan (ACP)
A comprehensive allergen management plan (ACP) is the foundation of an effective allergen management strategy. It involves identifying all allergens in the facility, setting clear protocols for handling and segregating allergenic ingredients, and ensuring that staff consistently follow the procedures.
In 2021, a study by The Institute of Food Technologists (IFT) revealed that nearly 50% of food manufacturers reported improvements in management after adopting formal allergen control plans. A well-structured ACP should outline critical control points, actions to prevent cross-contamination, and corrective measures in case of a deviation.
Folio3 FoodTech ERP can help by centralizing allergen data, providing real-time tracking of ingredients, and ensuring compliance with allergen control measures across all departments.
2. Implement Segregation Strategies
One of the most effective ways to prevent allergen cross-contact is by implementing segregation strategies. This includes designating separate areas, equipment, or storage spaces for allergenic ingredients and products. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) emphasize that investing in dedicated equipment and designating areas for preparing allergen-free food can significantly reduce cross-contact risk.
Using Folio3 FoodTech ERP, manufacturers can manage and track inventory in real-time, ensuring that allergenic ingredients are kept separate. The software allows manufacturers to create specific storage and handling guidelines for each allergen, improving traceability and reducing cross-contact risk. Allergen software also helps ensure that raw materials and finished products containing allergens are correctly segregated.
3. Enhance Cleaning and Sanitation Protocols
Cleaning and sanitation are vital aspects of allergen control management. After processing allergenic ingredients, thorough cleaning protocols are essential to eliminate traces of allergens and prevent contamination in subsequent production batches.
The European Food Safety Authority emphasizes that inadequate hygiene practices during food handling and processing can significantly contribute to contamination. Food manufacturers should implement routine cleaning schedules, validate cleaning effectiveness, and use allergen-specific cleaning agents to address this.
Folio3 FoodTech ERP can streamline cleaning processes by scheduling automated cleaning tasks, tracking cleaning cycles, and documenting validation checks to ensure all equipment is adequately cleaned between batches. Additionally, the system can flag potential risks and provide real-time reports on cleaning compliance.
4. Train Staff Effectively
Proper training is crucial in reducing allergen risks. Employees must understand the significance of managing allergens, the specific allergens in the facility, and the procedures for preventing cross-contamination.
Inadequate training contributed to over 30% of allergen-related incidents. Regular, ongoing training ensures that employees can safely handle allergens and recognize potential contamination signs. Folio3 FoodTech ERP supports training initiatives by providing access to training modules and tracking employee progress.
The software can store allergen procedures, making them easily accessible for all employees, and automate reminders for refresher courses. This ensures that staff remains updated with the latest allergen practices.
5. Accurate Labeling and Communication
Accurate allergen labeling is essential for consumer safety and regulatory compliance. Food manufacturers are required by law to list all significant allergens on product labels clearly, and failure to do so can result in serious health consequences for consumers, not to mention recalls and lawsuits.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture reported that in 2019, undeclared allergens were responsible for 45% of all food recalls. To mitigate such risks, manufacturers should implement robust systems for tracking ingredient sourcing, allergen declarations, and label updates, ensuring compliance with regulations like the Food Allergen Labeling and Consumer Protection Act (FALCPA).
With Folio3 FoodTech ERP, allergen information is seamlessly integrated into the system, ensuring accurate labeling data. The software allows manufacturers to maintain detailed ingredient records, track allergen declarations, and update product labels automatically, ensuring that all allergen information is accurate and compliant with industry standards.
6. Monitor and Audit Processes
Continuous monitoring and auditing are critical components of any solution. Regular food safety audits help identify gaps, track allergen control effectiveness, and ensure internal and external standards compliance. Auditing practices include checking allergen control measures, validating cleaning processes, and reviewing staff training records.
With Folio3 FoodTech ERP, manufacturers can automate audit processes by generating reports on allergen control measures, tracking compliance with cleaning schedules, and reviewing training histories. This system makes it easier to pinpoint areas for improvement and ensure consistency across the entire operation.
The Role of Technology in Streamlining Allergen Management
Relying solely on manual systems can expose businesses to significant risk in an era of increasing product complexity and stricter food safety regulations. For food manufacturers, integrating digital tools like ERP systems is becoming essential to ensure compliance, transparency, and consumer trust.
Why do Manual Processes Fall Short?
Managing allergens manually—through spreadsheets, paper records, or essential software—is time-consuming and prone to human error. A single oversight in documentation or labeling can result in allergen contamination, regulatory violations, or costly recalls. According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), undeclared allergens were the leading cause of food recalls in 2023, accounting for over 44% of all recall events.
As food supply chains grow more complex, it becomes nearly impossible to ensure effective allergen control management without digital support. Manual systems often struggle to:
- Track allergens across multiple production lines
- Maintain consistent allergen management labeling.
- Handle dynamic changes in supplier ingredients.
- Ensure traceability from raw materials to final products.
How Folio3 FoodTech ERP Systems Solve Allergen Challenges?
Folio3 FoodTech ERP offers a strong allergen management feature tailored to meet these growing food manufacturing and production demands. The platform helps businesses execute a consistent, data-driven allergen management plan that simplifies compliance and boosts food safety.
Key Features
The features include:
- Real-Time Traceability: With end-to-end tracking, manufacturers can trace allergenic ingredients from suppliers through processing to the shelf. This improves transparency and supports specific food management of allergens, especially in facilities handling multiple products.
- Automated Labeling: The ERP system automates allergen labeling by pulling accurate data from the formulation database. This ensures that every product is labeled correctly, minimizing the risk of mislabeling and supporting compliance with allergen regulations like FALCPA or EU Regulation No. 1169/2011.
- Inventory Management: Folio3’s ERP helps digitally segregate allergenic and non-allergenic materials, avoiding cross-contamination at every stage. It also supports food manufacturing and production management by tracking allergens at the batch, SKU, and storage levels.
- Audit Readiness: The system provides on-demand reports and dashboards for internal quality checks or external inspections. Manufacturers can easily demonstrate compliance with their allergen management policy, maintain documentation, and respond swiftly to auditor queries.
Benefits of Integration
Integrating a specialized ERP like Food ERP into your production environment transforms the management of allergens from a reactive task into a proactive strategy. Key benefits include:
- Reduced Risk of Recalls: Through automated processes and real-time alerts.
- Enhanced Regulatory Compliance: With digital logs, traceability, and complete allergen documentation.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Less manual work, faster audits, and more transparent oversight of allergen control points.
- Stronger Consumer Trust: Accurate management of allergen labeling reassures customers and protects brand integrity.
Regulatory Compliance – Staying Ahead of the Curve
Complying with allergen-related regulations is not optional for food manufacturers—it’s a legal and ethical obligation. With global standards evolving and consumer sensitivities rising, implementing a strong allergen management policy backed by thorough documentation and updated protocols is essential. Here’s how different regions are shaping the industry of food allergens.
U.S. Standards – FDA Regulations and the FASTER Act
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a key role in allergen oversight in the United States. The Food Allergy Safety, Treatment, Education, and Research (FASTER) Act, passed in 2021, officially added sesame as the ninth major food allergen.
As of January 1, 2023, all packaged foods must declare sesame clearly on the label, aligning with the existing Food Allergen Labeling and Consumer Protection Act (FALCPA). Failing to follow these regulations can result in recalls. The FDA reported that undeclared allergens accounted for 47.2% of all food recalls in 2023, making it the most common reason for market withdrawals.
Manufacturers are now required to:
- Identify sesame in both ingredients and processing aids.
- Use clear, standardized allergen management labeling.
- Maintain documented control over allergen exposure points.
Canadian Guidelines – Practical Tools from Food Allergy Canada
Canada’s approach to allergen regulation emphasizes education and prevention. The Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) requires food companies to declare the presence of priority allergens, gluten sources, and added sulfites.
Canadian manufacturers are also encouraged to use software to monitor and document procedures, enhancing traceability across the supply chain. Food Allergy Canada provides a detailed Allergen Management Checklist, helping businesses:
- Evaluate gaps in their allergen management plan.
- Train staff on specific food allergen management practices.
- Maintain strict control over cleaning and cross-contact zones.
Australian Context – Food Standards from FSANZ
In Australia and New Zealand, allergen rules are governed by Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ). Businesses must comply with Standard 1.2.3 – Mandatory Declarations, which requires clear labeling of allergens such as eggs, fish, milk, peanuts, sesame seeds, soybeans, tree nuts, and gluten-containing cereals.
FSANZ mandates:
- Clear identification of allergens in ingredient lists.
- A written AM policy covering procurement to packaging.
- Implementation of allergen control management across all production stages.
Recent audits reveal that labeling inaccuracies and poor training are among the leading causes of allergen-related violations. This underscores the importance of continuous staff training and real-time monitoring—two areas where digital allergen management solutions like ERP systems can be game-changers.
Global Trends – EU FIC and Codex Alimentarius
For international food manufacturers, compliance doesn’t stop at local regulations. The EU Food Information to Consumers (FIC) Regulation No. 1169/2011 mandates the clear highlighting of 14 major allergens in ingredient lists. These rules are strictly enforced across the European Union.
Meanwhile, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, a global food standards body jointly run by the WHO and FAO, outlines general principles for AM in food manufacture and production. Though not legally binding, Codex standards are widely referenced in international trade and inspections.
Many companies now invest in centralized allergen software to meet these global expectations. Tools like Folio3’s FoodTech ERP allow for seamless integration of allergen tracking, documentation, and real-time alerts, ensuring compliance with domestic and international standards.
Fix the Gaps in Your Operations
with an ERP That Speaks Food
We help food businesses move from generic or patchworked systems to a fully
integrated ERP, purpose-built for the industry, and designed for you.
Talk to Our Food ERP Specialist
Conclusion
Strong allergen management is both best practice and essential for business in the tightly regulated food industry. With undeclared allergens causing nearly half of food recalls in 2023, a clear AM plan is more urgent than ever.
Every step counts, from enforcing a solid allergen management policy to using advanced software. Consistency is key in refining your allergen control management protocols or ensuring accurate labeling.
Manufacturers can confidently protect consumers and maintain compliance in global markets by prioritizing food allergen management in sourcing, production, and packaging.
FAQs
What Is Allergen Management?
Allergen management refers to food manufacturers’ processes and policies for identifying, controlling, and preventing cross-contact of allergens during production. It ensures consumer safety and regulatory compliance.
What Are 5 Ways To Manage Food Allergies?
Key strategies include proper allergen labeling, ingredient segregation, staff training, thorough cleaning protocols, and implementing an allergen management plan.
What Are The Objectives Of Allergen Management?
The main goals are to prevent allergen cross-contact, ensure accurate labeling, protect allergic consumers, and comply with food safety regulations.
What Is The Allergen Risk Management Plan?
An allergen risk management plan outlines measures to identify allergenic hazards, assess their risks, and implement controls throughout the food production process.