We are part of a highly competitive and regulated environment, and the supply chain in the food industry has become a critical factor in ensuring operational success and customer satisfaction. The food supply chain is more than just a series of steps for food processors.
It’s a complex network involving procurement, production, distribution, and logistics, all of which must operate seamlessly to meet stringent quality and safety standards. But what is the food supply chain, and why is it incredibly challenging for food processors?
At its core, it encompasses everything from sourcing raw ingredients to delivering finished products to end consumers. However, the supply chain food industry faces unique hurdles, including fluctuating demand, perishable goods, regulatory compliance, and global disruptions. These challenges make effective food supply chain management vital for maintaining efficiency, minimizing waste, and ensuring food safety at every stage.
Key innovations in food supply chain solutions, such as real-time tracking, predictive analytics, and advanced logistics systems, transform how food processors navigate these challenges. By optimizing food supply chain logistics and implementing data-driven strategies, businesses can better control their operations and ensure sustainability, cost efficiency, and compliance.
Understanding the details of food industry supply chain management is essential for overcoming today’s challenges and preparing for tomorrow’s demands. Let’s explore how technology, strategic planning, and industry best practices are reshaping the landscape of food supply management and driving excellence across the food industry supply chain.
What is Food Supply Chain Management?
Food supply chain management is the systematic approach to overseeing the movement of food products, resources, and information across all stages, from farms to consumers. Traditional supply chain management involves managing people, assets, and processes.
However, supply chain management in food industry is uniquely complex due to the perishability of food items, the critical importance of safety standards, and the need for precise timing. Unlike standard supply chains, food supply chain management demands heightened attention to detail.
Timing is pivotal, as delays can directly impact food safety and quality. For instance, disruptions in food supply chain logistics due to transportation delays, inefficient cold chain management, or unmet Service-Level Agreements (SLAs) can lead to spoilage, increased costs, and dissatisfied customers. End-to-end visibility across the supply chain food industry is essential to mitigate such risks and maintain operational efficiency.
Failure to effectively in the food industry manage the supply chain management in food industry can have dire consequences. A single instance of foodborne illness caused by spoiled products could tarnish a company’s reputation, incur financial losses, and even lead to lawsuits. This highlights the critical role of food supply chain solutions in ensuring compliance with food safety and quality regulations while protecting the brand’s integrity.
Objectives of Food Supply Chain Management
The goals of supply chain management in food industry are multifaceted:
- Ensure Quality and Safety Compliance: Adhere to local and global standards to meet consumer and regulatory expectations.
- Minimize Costs: To maintain a cost-effective operation, address issues like inefficient routing, inventory mismanagement, and cold chain disruptions.
- Improve Communication: To avoid delays and quality complaints, improve coordination between production, processing, logistics, and other departments.
- Optimize Inventory Levels: Balance supply and demand effectively to reduce waste and prevent stockouts.
- Reduce Transportation Delays: Simplify shipping, documentation, and customs clearance to ensure timely delivery.
So, what is food supply chain management? It’s the backbone of the supply chain in food industry, orchestrating productivity, processing, quality assurance, and the flow of raw materials to achieve a seamless “farm to fork” process. A well-managed food supply management system prevents delays and inefficiencies and builds trust, ensuring consumers receive safe, high-quality food.
Key Components of Food Supply Chain Management
Effective supply chain management in food industry hinges on several interconnected components, each playing a vital role in ensuring the seamless flow of goods and information:
- Suppliers: Farmers and raw material providers supply the essential ingredients needed for food production.
- Manufacturers/Processors: These entities transform raw materials into finished or semi-finished products, maintaining quality and safety standards.
- Distributors: Logistics providers and wholesalers handle food supply chain logistics, ensuring products reach their intended destinations efficiently.
- Retailers: Supermarkets, grocery stores, and other outlets serve as the consumer-facing segment of the food industry supply chain.
- Consumers: The ultimate end-users of food products, whose expectations drive the need for transparency, quality, and timeliness.
Flow of Goods and Information
In the food supply chain, products and data flow through each component, requiring seamless communication and collaboration. Transparency and real-time communication are critical in food supply chain management to avoid delays, reduce waste, and ensure food safety.
Utilizing advanced food supply chain solutions fosters collaboration, offers end-to-end visibility, enhances efficiency, and builds trust throughout the supply chain food industry.
By effectively integrating these components, food industry supply chain management optimizes the journey from farm to fork, ensuring that products meet consumer demands while maintaining safety and quality standards. For instance:
- Goods move from farms to processors through distributors and retailers before reaching consumers.
- Information about demand, inventory levels, and compliance requirements travels in opposite directions, guiding decision-making at each stage.
What Are the Challenges in Food Supply Chain Management?
Food supply chain management faces numerous complexities that can disrupt the seamless flow of goods and information across the supply chain food industry. Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
However, with the help of advanced food supply chain solutions can help navigate these complexities, providing a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market. By overcoming the following challenges, businesses can simplify their supply chain in food industry, ensuring that food products are delivered safely, efficiently, and sustainably from farm to fork:
1. Perishability of Products
Food products are highly perishable, requiring precise handling and storage conditions to maintain quality and prevent spoilage. Food supply chain logistics challenges, such as delays or cold chain failures, can lead to significant losses. Effective food supply chain solutions are essential to minimize waste and extend product shelf life.
2. Food Safety and Quality Assurance
Ensuring food safety and meeting quality standards are critical aspects of supply chain management in the the food industry. Contaminated or spoiled food can pose health risks and damage a company’s reputation. Compliance with safety protocols and end-to-end traceability are vital for mitigating these risks.
3. Regulatory Compliance
The supply chain management in food industry is subject to stringent local and international regulations. From labeling requirements to health inspections, businesses must navigate complex compliance frameworks. Failing to adhere to these regulations can result in penalties, recalls, and loss of consumer trust.
4. Supply Chain Disruptions
Disruptions such as transportation delays, natural disasters, or geopolitical issues can severely impact food supply management. For example, food supply chain logistics delays can lead to stock shortages or quality degradation, highlighting the need for resilient and flexible supply chain strategies.
5. Sustainability Concerns
Sustainability has become a priority in food industry supply chain management. Companies must address challenges such as reducing carbon emissions, minimizing packaging waste, and promoting ethical sourcing practices. Incorporating sustainable practices improves environmental impact and aligns with consumer demands for eco-friendly products.
How to Address Food Supply Chain Challenges? – Strategies for Effective Food Supply Chain Management
Overcoming challenges in supply chain management in food industry requires adopting innovative strategies and using advanced tools. With these strategies, businesses can overcome common challenges in the supply chain in food industry, ensuring a resilient and efficient system that meets consumer demands while maintaining safety and sustainability standards.
Advanced food supply chain solutions empower companies to achieve their goals and gain a competitive edge in an evolving marketplace. Here are some effective methods to improve food supply chain management and ensure efficiency, safety, and sustainability:
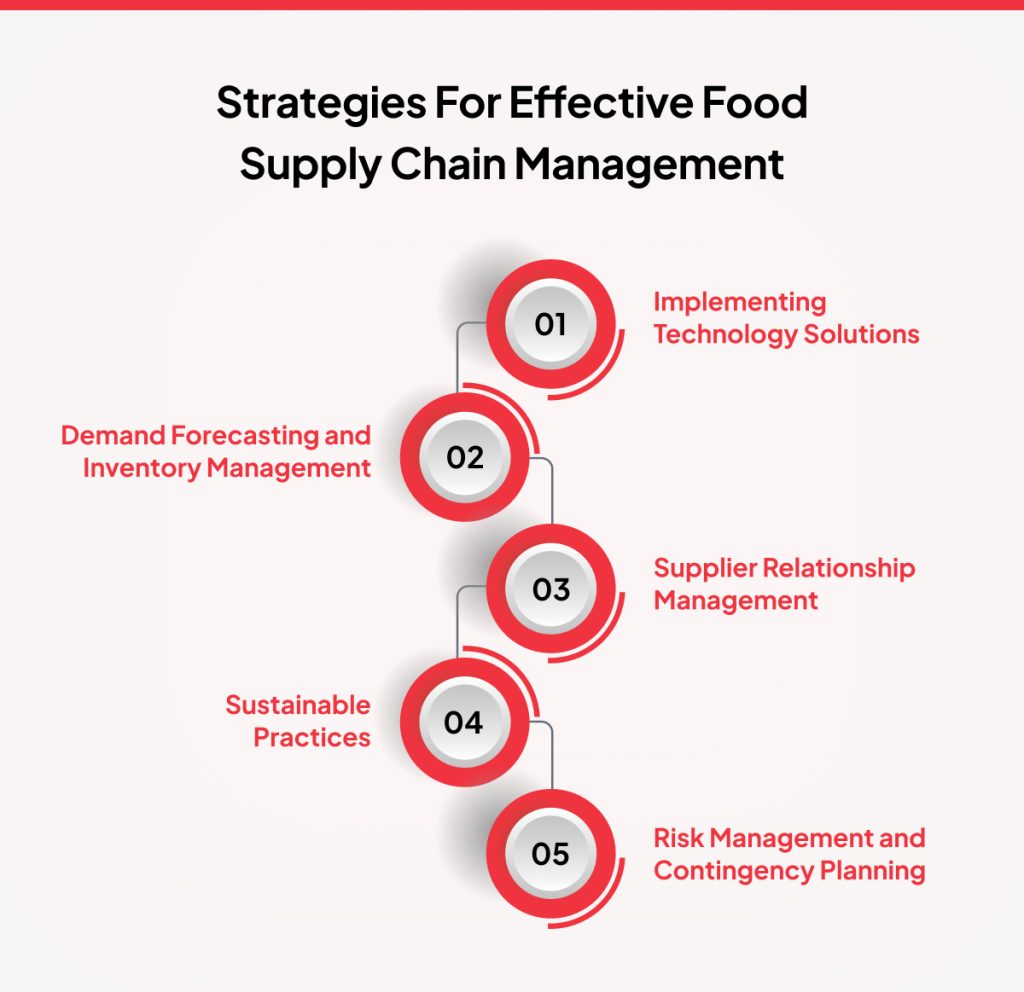
1. Implementing Technology Solutions
Incorporating advanced technologies is pivotal for optimizing supply chain management in food industry. Tools like Food ERP, IoT devices, and blockchain enable seamless operations, improve traceability, and ensure product safety across the food supply chain. These innovations provide real-time data and insights, empowering businesses to address inefficiencies, reduce risks, and effectively meet consumer demands.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems simplify operations across the food industry supply chain. They offer integrated solutions for tracking inventory, order management, and compliance monitoring.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Devices: IoT devices monitor temperature, humidity, and storage conditions, ensuring product safety throughout food supply chain logistics.
- Blockchain for Traceability: Blockchain technology enhances transparency in food supply chain solutions, enabling traceability from farm to fork. It helps build consumer trust by verifying product authenticity and compliance with safety standards.
2. Demand Forecasting and Inventory Management
Accurate demand forecasting and optimized inventory management prevent overstocking or understocking issues. Predictive analytics tools help align production with market demand, ensuring smooth operations across the supply chain food industry.
3. Supplier Relationship Management
Strong relationships with suppliers are crucial for seamless food supply management. Collaborative planning, timely communication, and shared quality standards reduce the risks of delays and ensure consistency in raw material availability.
4. Sustainable Practices
Adopting sustainable practices is essential for modern supply chain management in food industry. Businesses can create a more resilient and environmentally responsible food supply chain by reducing the carbon footprint, minimizing food waste, and promoting eco-friendly sourcing. These practices support global sustainability goals and improve brand reputation and long-term profitability.
- Reducing Carbon Footprint: Efficient logistics planning, such as optimizing delivery routes and adopting renewable energy sources, minimizes the environmental impact of the food industry supply chain.
- Waste Reduction Initiatives: Implementing strategies to reduce food waste at the production, processing, and retail stages supports sustainability goals and cost savings in food supply chain management.
5. Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Developing robust risk management strategies is essential to mitigate potential food supply chain logistics disruptions. Contingency plans, including alternate suppliers and flexible delivery routes, ensure business continuity during unforeseen events.
The Role of ERP in Food Supply Chain Management
Effective food supply chain management is critical for addressing the unique challenges faced by food processors, including perishable inventory, strict regulatory requirements, and fluctuating consumer demands.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems organize and integrate processes, enabling businesses to enhance efficiency, compliance, and customer satisfaction. Here’s how food ERP systems play a transformative role in food supply chain management:
Integration of Processes
ERP systems act as a centralized platform, connecting various supply chain functions, such as procurement, inventory management, production, and distribution. This seamless integration ensures:
- Procurement Management
Automating and optimizing purchase order management, vendor cataloging, and invoice processing. Features such as:
- Purchase Order Management: Automates creating and tracking purchase orders, ensuring the timely procurement of raw materials.
- Vendor Catalog Management: Centralizes supplier information, improving coordination and simplifying reordering.
- Purchase Invoicing and Discounts: Organizes invoicing workflows and ensures cost-saving opportunities through line-item discounting.
- Inventory Management
Facilitates precise tracking of stock levels, attributes, and storage conditions with features such as:
- Lot Tracking and Expiry Management: Ensures product freshness and compliance by monitoring expiration dates and lot numbers.
- Allergen Visibility and Catch Weights: Maintains transparency for allergen information and variable product weights.
- Stock Keeping Units (SKUs) and Location Transfers: Tracks inventory across multiple locations, improving inventory accuracy and availability.
- Supply Planning
Enhances production and delivery planning with:
- Demand Forecasting: Predicts customer demand based on historical data and market trends.
- Order Promising and Master Production Scheduling: Ensures timely order fulfillment by aligning production schedules with supply chain activities.
Real-Time Data and Analytics
One of the most significant benefits of ERP systems is their ability to deliver real-time insights into supply chain operations. For instance, by using real-time data, businesses can reduce food spoilage, optimize delivery schedules, and improve operational efficiency. Food processors gain:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Access to up-to-date inventory, production, and sales data improves responsiveness to market changes.
- Performance Monitoring: Analytics tools like Power BI help identify inefficiencies and drive continuous improvement.
- Predictive Analytics: Anticipates supply chain disruptions and enables proactive decision-making, ensuring smoother operations.
Compliance and Reporting
Regulatory compliance is non-negotiable in the food industry. These features protect businesses from regulatory penalties and enhance their reputation for delivering safe, high-quality products. ERP systems simplify compliance management by:
- Tracking Regulatory Requirements: Maintaining detailed records of allergens, lot numbers, and expiry dates ensures adherence to food safety standards.
- Automating Audit Trails: Ensuring transparent and traceable records for inspections and certifications.
- Custom Reporting Tools: Generating comprehensive compliance reports for governing bodies and stakeholders.
Success Stories in Food Supply Chain Management
The following case study is about solving purchase order inefficiencies with custom NetSuite solutions for better accuracy, transparency, and customer service:
About Sundia Corporation
Sundia Corporation is one of North America’s fastest-growing fruit produce brands, offering fresh produce and ready-to-eat organic fruit cups. With a strong distribution network across the U.S., Canada, the Philippines, India, and China, Sundia is committed to promoting healthier lifestyles through nutritious and high-quality products.
Understanding the Challenge – Overcoming Operational Inefficiencies
Sundia Corporation faced significant challenges managing its supply chain, particularly in processing electronic purchase orders (POs). Key issues included:
- PO Splitting Issues: Multiple POs from the same customer were received in a single file, causing processing delays.
- Lack of Readability: POs in EDI format were not human-readable, complicating verification and storage.
- Dispute Resolution Difficulties: Limited visibility into PO details hindered dispute resolution regarding order quantities and pricing.
Building the Solution
Folio3 developed a customized NetSuite Suitelet to address Sundia’s challenges, delivering a tailored solution for improved efficiency and transparency:
- Automated PO Splitting: Enabled seamless splitting of multiple POs into individual files for efficient processing.
- Enhanced Readability: Converted EDI-format POs into easily referenceable PDFs.
- Organized Order Association: Linked POs with corresponding orders to provide end-to-end visibility.
- Real-Time Alerts: Integrated email notifications to keep stakeholders informed of transaction statuses.
Results – Transforming Operations and Elevating Customer Service
The custom solution delivered measurable improvements:
- Improved Visibility: Complete transparency into purchase orders, reduced processing errors, and enhanced operational accuracy.
- Efficient Dispute Resolution: Readable and traceable POs enabled swift resolution of order and pricing disputes.
- Automated Workflows: Reduced manual efforts with automated PO splitting and real-time notifications.
- Scalable Integration: A robust system supporting Sundia’s growth while maintaining operational excellence.
Best Practices for Food Processors
Food processors must adopt best practices that optimize operations, improve safety, and meet consumer demands to stay competitive and maintain an efficient and sustainable food supply chain. By adopting these best practices, food processors can simplify operations, enhance food safety, and build a more resilient food supply chain.
These efforts contribute to better product quality, reduced waste, and increased customer satisfaction while ensuring long-term success in the competitive food supply chain industry. Here are some of the most effective strategies for enhancing supply chain management in food industry:
1. Adopting Lean Manufacturing Principles
Implementing lean manufacturing principles helps food processors eliminate waste, reduce costs, and improve operational efficiency across the food supply chain.
By focusing on value-added activities and minimizing unnecessary processes, companies can simplify their production lines and improve food supply chain management. Lean practices also help improve quality control and consistency, which are vital in the food industry supply chain.
2. Ensuring Cold Chain Integrity
Cold chain integrity is crucial in the food supply chain logistics, particularly for perishable goods. Ensuring the proper storage, transportation, and handling of temperature-sensitive products helps maintain food safety, quality, and freshness.
Temperature monitoring technologies and the establishment of robust cold chain procedures can help food processors ensure that their products remain safe throughout the food supply chain and reduce spoilage and waste.
3. Employee Training and Development
A well-trained workforce is key to the success of any food supply chain management strategy. Food processors must invest in continuous training and development to ensure their employees can handle evolving technologies, food safety standards, and industry regulations.
Regular training programs help mitigate risks, improve safety practices, and foster a culture of quality and compliance, which is essential for maintaining the integrity of the food supply chain.
4. Continuous Improvement and Innovation
Continuous improvement is a hallmark of successful supply chain management in food industry. By adopting a culture of innovation, food processors can improve operational efficiency food safety, and meet changing market demands.
To stay ahead of the competition, processes must be regularly assessed, feedback sought, and new technologies incorporated. New food supply chain solutions, such as AI, IoT, and blockchain, can further improve transparency, traceability, and decision-making within the food industry supply chain.
FAQs
What Is Supply Chain Management In Food Industry, & Why Is It Important?
Supply chain management in food industry involves overseeing the flow of food products from farm to table, including production, processing, storage, transportation, and distribution. It is crucial to ensure food safety, quality, cost efficiency, and timely delivery while minimizing waste and meeting regulatory requirements.
How Does Supply Chain Management In The Food And Beverage Industry Work?
Supply chain management in the food and beverage industry integrates procurement, production, inventory, and distribution to maintain freshness and quality. Technologies like ERP systems and IoT enhance efficiency.
How Does ERP Software Improve Supply Chain Management In Food Industry?
ERP systems simplify supply chain processes by offering real-time tracking, inventory management, demand forecasting, and compliance monitoring. They integrate data across departments, helping businesses make informed decisions, minimize waste, and optimize resources.
How Do Fast Food Chains Handle Supply Chain Disruptions?
Fast food chains often rely on multiple suppliers, maintain safety stock, and use technology to monitor the supply chain in real-time. During disruptions, they prioritize critical products and adapt menus to utilize available ingredients while maintaining quality and service.