Ensuring food safety, regulatory compliance, and supply chain transparency is paramount in the food manufacturing industry. Consumers demand assurance that the products they consume are safe and sourced responsibly. Regulatory bodies are enforcing stricter compliance requirements, and the globalization of supply chains has introduced complexities that necessitate robust traceability in food industry systems.
Technological advancements are revolutionizing food traceability. Innovations such as blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, and artificial intelligence (AI) are being utilized to enhance traceability in food industry, providing real-time visibility and data accuracy throughout the food supply chain. These technologies enable precise tracking of products from origin to the consumer, improving food safety and operational efficiency.
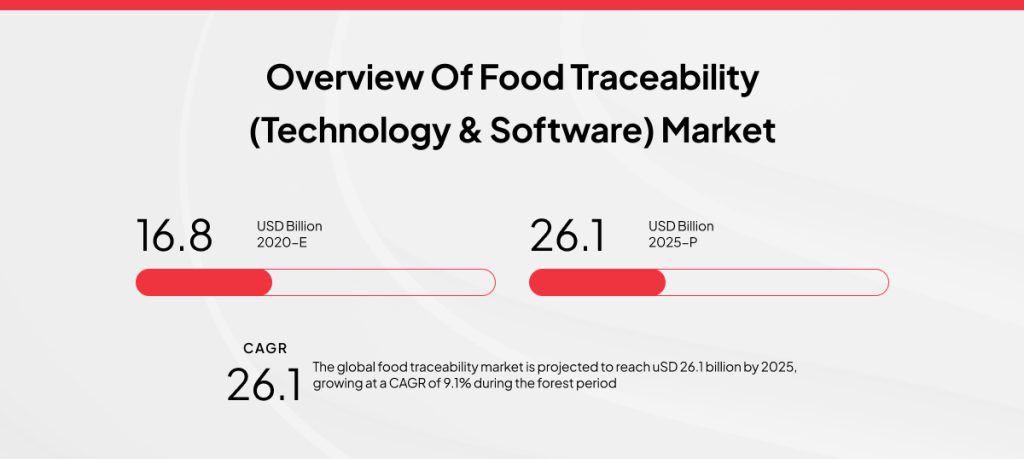
The global food traceability market reflects this technological integration and growing emphasis on safety and transparency. According to MarketsandMarkets, it is valued at USD 16.8 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 26.1 billion by 2025, recording a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.1%.
This blog will delve into food traceability, its significance in the industry, and how implementing a comprehensive traceability system can enhance food safety and compliance.
What Is Food Traceability?
Food traceability refers to the ability to track the movement of food products through every stage of production, processing, and distribution. It ensures that every ingredient and product can be traced back to its source and final destination, enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to safety concerns, recalls, and regulatory requirements.
Two Key Types of Food Traceability
- Backward Traceability
Backward traceability in food industry involves tracking raw materials, ingredients, and components to their source. This helps manufacturers verify supplier compliance, ensure quality standards, and quickly identify the root cause of contamination in case of food safety incidents.
- Forward Traceability
Forward traceability in food industry tracks finished products from the manufacturer to the end consumer. This enables companies to pinpoint the locations of distributed goods, making it easier to recall affected products if necessary.
Real-World Example – Tracing Contaminated Lettuce in a Recall
In 2018, an E. coli outbreak linked to romaine lettuce sickened over 200 people in the U.S. and Canada. Without an efficient food traceability system, it took weeks to identify the contaminated source. Today, with advanced traceability in food industry, manufacturers can use digital tracking tools to trace contaminated produce back to specific farms within hours, significantly reducing health risks and economic losses.
A well-integrated traceability system in the food industry enhances food safety and traceability and reduces the chances of food safety failures.
Why Is Food Traceability Important?
Implementing traceability in food industry is more than just a regulatory requirement—it is essential for food safety, compliance, consumer trust, and waste reduction. A well-designed food traceability system helps manufacturers mitigate risks, improve efficiency, and maintain brand integrity. Let’s explore why traceability in food industry is crucial.
a) Ensures Food Safety and Prevents Contamination
Foodborne illness outbreaks can have devastating consequences for public health and business operations. Food traceability enables manufacturers to identify and isolate contaminated products swiftly, preventing them from reaching consumers.
- Quick Recalls: A traceability system for food manufacturing helps companies pinpoint affected batches and remove them from distribution in record time, reducing the spread of contamination.
- Prevention of Foodborne Illness: Companies can detect potential hazards before they escalate into outbreaks by tracking raw materials and finished products.
b) Helps With Regulatory Compliance
Food traceability is a legal requirement in many countries, with governments enforcing strict regulations to ensure public safety.
Key Global Food Traceability Regulations
- U.S.: The FDA’s Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) mandates enhanced traceability in food supply chain, requiring detailed record-keeping of food movement.
- European Union: EU laws require all food businesses to establish traceability systems in the food industry under the General Food Law Regulation (EC 178/2002).
- Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI): A benchmark for international food safety standards, promoting food safety and traceability in food industry best practices.
Non-Compliance Risks
Failure to comply with these regulations can result in severe consequences, including hefty fines, product bans, lawsuits, and reputational damage.
c) Builds Consumer Trust and Brand Reputation
Consumers today demand greater transparency in food sourcing and production. A robust food traceability system fosters trust by ensuring ethical sourcing and high-quality standards.
- Transparency in Sourcing: Consumers want to know where their food comes from, how it was processed, and whether it meets safety and sustainability standards.
- Ethical Sourcing & Sustainability: The demand for responsibly sourced products is growing, and consumers prefer brands that prioritize food safety and traceability in food industry.
d) Reduces Food Waste and Prevents Fraud
Food fraud and waste are growing concerns for the industry. An advanced traceability system in food industry operations helps manufacturers identify inefficiencies, prevent counterfeit food products, and minimize waste.
- Preventing Food Waste: Manufacturers can reduce spoilage and optimize inventory management by tracking expiration dates and supply chain inefficiencies.
- Combatting Food Fraud: Traceability in food industry helps detect mislabeled or counterfeit food products, protecting consumers from deception.
Challenges in Implementing Food Traceability
While traceability in food industry is essential for food safety, regulatory compliance, and consumer trust, implementing an effective food traceability system comes with several challenges. From complex supply chains to the high costs of technology adoption, food manufacturers must overcome significant hurdles to establish seamless traceability in food industry processes.
1. Complex Supply Chains
The modern traceability system for food manufacturing must account for an increasingly complex supply chain involving multiple suppliers, contract manufacturers, and global sourcing.
- Multiple Stakeholders: Ingredients and raw materials often pass through several intermediaries, making it difficult to track their origins.
- Global Sourcing Risks: International suppliers follow different food safety regulations, which may lead to inconsistencies in traceability in food supply chain.
2. High Costs of Technology Adoption
Upgrading to a digital traceability system in food industry operations requires substantial investment in hardware and software, such as:
- Barcode & RFID Systems: These technologies automate product tracking but require expensive infrastructure upgrades.
- Blockchain for Traceability: While blockchain ensures tamper-proof records, it requires high implementation costs and skilled IT professionals to manage.
3. Data Management and Integration Issues
Food manufacturers often operate with outdated legacy systems that do not integrate with modern food traceability system platforms, leading to:
- Disconnected Data Silos: Many companies still rely on manual record-keeping or standalone software, making end-to-end traceability in food industry is difficult.
- Inconsistent Data Entry: Errors in manual tracking can compromise the accuracy of traceability food safety records.
4. Standardization In Traceability Requirements
Different countries and industries have varying food safety and traceability regulations, making compliance challenging for food manufacturers operating across multiple markets.
- Diverse Regulatory Standards: The U.S. FSMA traceability rules differ from the EU’s General Food Law, creating complexities for global food businesses.
- Industry-Specific Requirements: The dairy, seafood, and meat industries have different traceability systems for food manufacturing standards, which adds to the compliance burden.
How Technology Is Transforming Food Traceability?
The rapid evolution of technology is revolutionizing traceability in food industry, making it more transparent, efficient, and secure. Digital innovations such as blockchain, IoT, RFID, and AI-driven analytics are helping food manufacturers overcome long-standing challenges in food traceability while ensuring compliance with global food safety regulations.
Technology reshapes food safety and traceability, enabling manufacturers to enhance compliance, reduce risks, and build consumer trust. By integrating blockchain, IoT, RFID, and AI-powered analytics, food manufacturers can streamline traceability systems for food manufacturing, ensuring food safety, regulatory compliance, and transparency across the entire food supply chain.
1. Blockchain for Transparent and Secure Food Tracking
Blockchain technology is reshaping food traceability systems by creating a decentralized, tamper-proof ledger that records every step of the traceability process of the food supply chain in food supply chain process.
How Does It Work?
- Blockchain records every transaction in real time, from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished products.
- Data stored on the blockchain cannot be altered, ensuring traceability food safety and preventing food fraud.
Example – IBM Food Trust
Walmart, Nestlé, and Carrefour have partnered with IBM Food Trust, a blockchain-based food traceability system, to enhance food safety. Walmart reduced the time it takes to trace contaminated lettuce from seven days to just 2.2 seconds, allowing faster recalls and minimizing health risks.
2. IoT and RFID for Real-Time Tracking
Internet of Things (IoT) devices and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology enable real-time monitoring of food products as they move through the supply chain.
How Does It Work?
- RFID tags & QR codes track food items from farm to shelf.
- IoT sensors monitor critical conditions such as temperature, humidity, and location.
- Automated alerts notify suppliers of deviations that could compromise food safety and traceability.
3. AI and Data Analytics for Traceability Optimization
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in food safety transforms food traceability systems by detecting supply chain inefficiencies, predicting risks, and enhancing food safety measures.
How Does It Work?
- AI-powered predictive analytics help manufacturers anticipate supply chain disruptions.
- Machine learning algorithms detect inconsistencies in food tracking, reducing fraud and contamination risks.
- Automated recall management enables swift action in the event of contamination.
How Does Food Safety Software Solve Traceability Challenges?
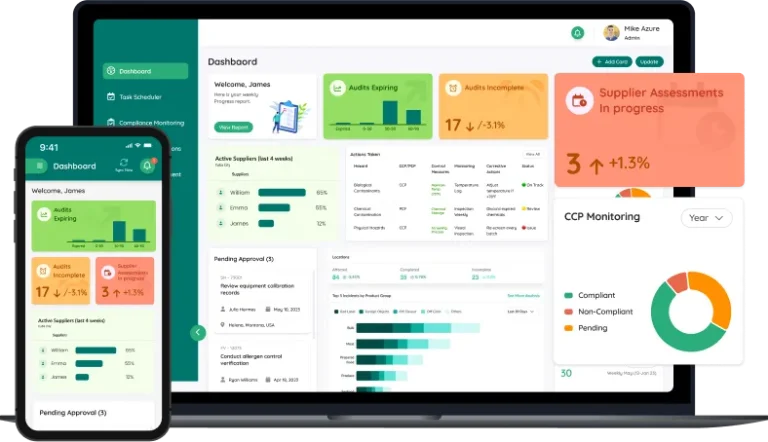
Implementing traceability in the food industry presents challenges such as complex supply chains, high technology costs, and data integration issues. Folio3’s Food Safety Software is built to help manufacturers overcome these hurdles, ensuring end-to-end traceability, real-time monitoring, and regulatory compliance while enhancing food safety and operational efficiency.
Why Choose Food Safety Software?
Food Safety Software provides a robust traceability system for food manufacturing, allowing businesses to seamlessly track raw materials, production processes, and finished goods.
The software helps manufacturers prevent contamination, reduce foodborne illness risks, and meet strict food safety regulations using advanced tracking, automation, and compliance tools. With the latest automation, real-time monitoring, and AI-powered insights, food traceability software helps food manufacturers build a safer, more transparent, and compliant supply chain.
Key Traceability Features of Food Safety Software by Folio3 FoodTech
FoodTech’s software is designed to streamline food traceability, enhance safety, and improve compliance while giving manufacturers real-time supply chain visibility. Here’s how it strengthens food safety and traceability:
1. Lot & Batch Tracking
- Tracks products from raw materials to consumers, ensuring full visibility in the food supply chain.
- Helps quickly identify and isolate contaminated batches, preventing widespread recalls.
2. Real-Time Supply Chain Monitoring
- Monitors food movement across warehouses, distribution centers, and retail shelves to ensure proper handling.
- Reduces food waste by optimizing inventory and preventing spoilage.
3. Automated Compliance Reporting
- Generates audit-ready reports for FDA, USDA, FSMA, and GFSI compliance effortlessly.
- Helps businesses avoid fines, recalls, and regulatory violations through real-time reporting.
4. IoT & Blockchain-Enabled Tracking
- IoT sensors monitor temperature, humidity, and location to ensure perishable foods remain safe.
- Blockchain integration guarantees tamper-proof record-keeping, securing traceability data for better transparency.
Conclusion – Strengthening Food Safety with Traceability
Food traceability is essential for safety, compliance, and consumer trust. Food manufacturers must adopt advanced traceability systems to stay competitive with stricter regulations and a growing demand for transparency.
Technology blockchain, IoT, AI, and ERP solutions is transforming traceability in food industry, making recalls faster, compliance easier, and supply chains more secure. Folio3 FoodTech ERP ensures end-to-end traceability, helping businesses meet regulations, reduce waste, and protect their brand.
FAQs
What Is The Importance Of Traceability?
Traceability ensures food safety, regulatory compliance, and consumer trust by tracking products across the supply chain.
What Is An Example Of Food Traceability?
Tracing contaminated lettuce during a recall helps identify the source and prevent further outbreaks.
What Are The Objectives Of Food Traceability?
Key objectives include improving food safety, ensuring regulatory compliance, preventing fraud, and enhancing supply chain transparency.
What Are The Important Factors Of Traceability?
Critical factors include lot tracking, real-time monitoring, compliance reporting, and supply chain integration.
What Is The Food Traceability Rule?
The FDA’s Food Traceability Rule mandates record-keeping for high-risk foods to ensure faster recalls and safety compliance.