Food traceability has always been at the heart of consumer trust and food safety, yet traditional systems still struggle to keep up with the complexity of modern supply chains. Many producers rely on manual tracking or fragmented databases, which makes it difficult to verify product origins, ensure quality, or respond quickly to recalls. These outdated food traceability technology tools often result in blind spots that can damage brands and compromise consumer safety. With one-third of all food produced globally wasted each year, stronger traceability systems are sorely needed to reduce loss and improve supply chain efficiency.
That’s where blockchain food traceability comes in. By using a secure, decentralized ledger, blockchain enables every stakeholder, including farmers, processors, distributors, and retailers, to record and access the same verified data in real time. Each transaction or movement of goods becomes traceable, tamper-proof, and permanently stored, giving consumers and regulators full visibility into where their food comes from and how it’s handled.
In this blog, we’ll explore how blockchain in food industry operations is transforming transparency and accountability across the value chain. You’ll learn how blockchain works in food traceability, its benefits for producers and consumers, real-world applications across sectors, key challenges, and how Folio3 FoodTech supports blockchain-driven innovation for safer and smarter supply chains.
Understanding Blockchain in the Food Industry
At its core, blockchain food traceability is a digital ledger system that records every step of a product’s journey, from farm to fork, in a secure and transparent way. Each transaction, whether it’s harvesting, processing, shipping, or storage, is recorded as a “block” of data linked chronologically to the next. This creates a permanent, tamper-proof record that can be accessed by authorized parties across the supply chain, improving both food safety and consumer trust.
Unlike traditional ERP or inventory tools that store data in isolated databases, blockchain in food systems operate on decentralized networks. This means no single participant can alter or delete information without consensus, reducing the risk of data manipulation or fraud. It ensures that all stakeholders, from growers and distributors to retailers and regulators, work from the same verified dataset, increasing transparency and accountability across every link in the chain.
In the traceability of food products, blockchain allows instant tracking of where an item originated, how it was handled, and under what conditions it was transported. For example, in the event of a contamination or recall, blockchain enables rapid tracing of affected batches within seconds rather than days. This level of precision strengthens food compliance with evolving global standards like FSMA 204, which requires enhanced recordkeeping for high-risk foods.
Ultimately, blockchain for food traceability modernizes how producers manage quality assurance and regulatory obligations, creating a more efficient and reliable framework for global food systems. By combining real-time visibility with immutable data, blockchain food traceability is redefining how trust is built and maintained in the blockchain food industry. Additionally, the use of decentralized IDs (DIDs) and verifiable credentials (VCs) for suppliers, certifiers, and auditors further strengthens authentication and accountability across the supply chain.
Key Benefits of Blockchain for Food Traceability
Transparency and Trust
One of the greatest advantages of blockchain food traceability is the ability to create complete transparency across the entire blockchain food supply chain. Every movement of food, from production and packaging to storage and distribution, is recorded in real time. This ensures that data is consistent, traceable, and available to all authorized stakeholders. Such visibility helps prevent fraud and mislabeling while promoting accountability throughout the traceability in the food industry ecosystem.
Food Safety and Recall Management
When contamination or food safety failures occur, rapid response is crucial. Blockchain enables instant access to detailed product histories, allowing producers and regulators to identify affected batches within minutes. This quick traceability minimizes waste, prevents widespread recalls, and protects public health. It also strengthens food safety audits by maintaining immutable records of every process, ensuring greater accuracy during inspections and compliance checks.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with evolving global regulations is a challenge for many food producers. Blockchain simplifies this by maintaining permanent, time-stamped records that verify each step of the supply chain. This aligns with mandates such as FSMA 204, which require detailed tracking for high-risk foods. As a result, blockchain in food industry operations can streamline documentation, reduce manual reporting, and meet strict international food safety and import standards with confidence.
Consumer Confidence
Modern consumers care deeply about where their food comes from and how it’s handled. Blockchain food traceability provides verifiable sourcing information that can be shared through QR codes or digital food labels. This transparency fosters trust and builds stronger brand loyalty by showing proof of authenticity, ethical sourcing, and sustainability. As more brands adopt blockchain food supply chain systems, consumers can make safer, more informed purchasing decisions based on verified product data.
Core Components of Blockchain Food Traceability Technology
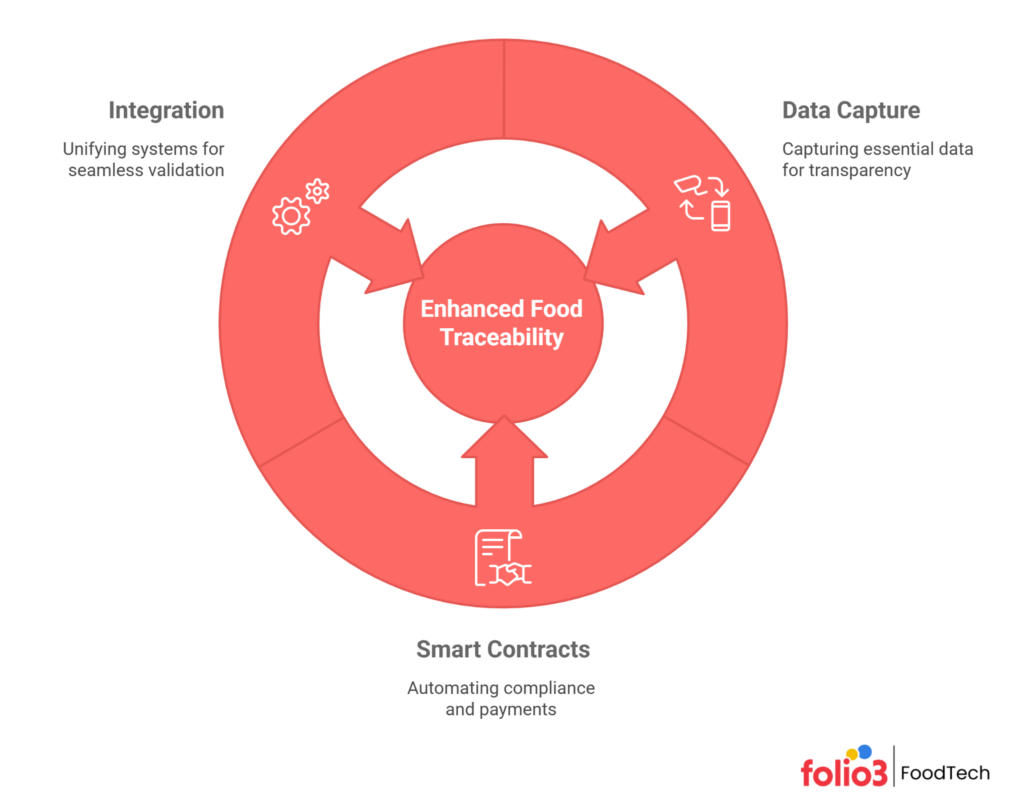
Data Capture: The Foundation of Transparency
Effective blockchain food traceability starts with accurate data capture. Modern blockchain food traceability technology relies on sensors, barcodes, RFID tags, and IoT devices to collect real-time data from every stage of the food supply chain. These technologies record details like temperature, location, and handling conditions, ensuring that no step in the process goes undocumented. Such integration supports broader food manufacturing trends focused on automation and digital monitoring, which help businesses improve accuracy and accountability.
Smart Contracts: Automating Compliance and Payments
Smart contracts are self-executing digital agreements built into the blockchain. In blockchain food traceability, they automatically trigger actions, such as payments, certifications, or shipment releases, once specific conditions like quality checks or temperature thresholds are met. This automation minimizes manual errors, reduces administrative delays, and ensures that compliance is upheld without constant supervision. By integrating these contracts into blockchain systems, the blockchain in food industry enhances both efficiency and transparency across producers, suppliers, and retailers.
Integration: Unifying Systems for Seamless Validation
The true power of blockchain food traceability lies in its ability to integrate seamlessly with ERP platforms, quality assurance systems, and logistics tools. When combined, these systems enable automatic validation of trace data, eliminating redundancies and reducing the risk of mismatched information. For instance, blockchain records can confirm whether cold chain standards were maintained during transport or whether safety tests were completed before distribution. This connectivity also supports food manufacturing waste reduction by providing clear insights into inefficiencies or spoilage points.
Key canonical flows include ERP systems for lots and purchase orders, WMS/TMS for shipping and receipts, LIMS/QA for certificates of analysis (COAs), and MES for product transformations. Event data from these systems is normalized and captured via EPCIS interfaces, ensuring consistent, interoperable records across the supply chain.
By combining smart data capture, automated smart contracts, and robust integration, blockchain food traceability delivers a holistic, interoperable framework that strengthens trust and efficiency across the modern food supply chain.
Real-World Use Cases Across the Food Industry
The adoption of blockchain food traceability is no longer experimental; it’s actively transforming how food companies manage safety, quality, and transparency. From dairy farms to seafood suppliers and plant-based producers, blockchain provides an auditable trail that enhances trust and minimizes risk throughout the blockchain food supply chain. Below are a few real-world examples of how the blockchain food traceability technology is driving tangible results across the food landscape.
Dairy & Beverages: Guaranteeing Origin and Freshness
In the dairy sector, blockchain food traceability helps verify milk origin, storage conditions, and transportation temperatures in real time. Leading beverage companies have implemented blockchain to track batches from farm to bottle, ensuring freshness and compliance at every checkpoint. This visibility prevents mishandling, supports regulatory audits, and gives consumers confidence that what they’re drinking meets the highest safety standards.
Seafood: Protecting Authenticity and Sustainability
Seafood fraud is a global issue, with mislabeled fish costing the industry billions each year. Blockchain technology is now being used to authenticate catch data, verify sustainability certifications, and ensure compliance with fishing quotas. By securing every transaction in the traceability of food products, blockchain eliminates data tampering and guarantees that only legally and ethically sourced seafood reaches the market.
Fresh Produce: Monitoring Harvest-to-Shelf Integrity
For perishable goods like fruits and vegetables, freshness depends on precise time and temperature tracking. Blockchain in food enables producers and retailers to monitor every step, from harvest to shelf, through integrated IoT sensors and digital records. If a temperature breach or delay occurs, the affected batch can be instantly identified and removed, preventing waste and improving overall supply chain efficiency.
Plant-Based Foods: Building Trust Through Transparency
Consumers of plant-based products demand clear sourcing information and proof of ethical production. Blockchain addresses this by recording every ingredient’s origin and processing step on an immutable ledger. This strengthens consumer confidence and helps brands differentiate through verified sustainability claims.
In each of these sectors, blockchain food traceability strengthens visibility, prevents fraud, and boosts operational efficiency. By embedding blockchain into the blockchain food supply chain, companies are not only improving compliance and safety but also reshaping how trust is built within the global food ecosystem.
Challenges and Limitations
While blockchain food traceability offers immense potential for improving transparency, efficiency, and accountability across the food supply chain, it also faces several challenges that must be addressed before full-scale global adoption can occur. These challenges are not just technical but also financial and regulatory, requiring collaboration among producers, technology providers, and policymakers.
Data Accuracy
Blockchain ensures transparency and immutability, but the quality of the data entered still determines the system’s overall reliability. If incorrect or incomplete information is logged, even the most advanced blockchain for food traceability system cannot correct those errors. This is often referred to as the “garbage in, garbage out” problem. For instance, if a supplier inputs the wrong batch number or shipment date, that misinformation becomes a permanent part of the blockchain record. To counter this, food companies increasingly rely on IoT devices, smart sensors, and automated data capture systems that minimize human error. Integration with these technologies helps ensure that blockchain networks store only verified, real-time data, which is crucial for maintaining traceability integrity.
Cost Barriers
While the long-term benefits of blockchain food traceability are clear, the initial costs can be prohibitive, particularly for small and mid-sized producers. Implementing blockchain requires investment in digital infrastructure, employee training, and often collaboration with multiple supply chain partners. Smaller producers may also face challenges in accessing the technical expertise needed to set up and maintain these systems. To address these challenges, scalable and cloud-based blockchain solutions are being developed, enabling pay-as-you-go access and reducing upfront costs. Still, until these options become more mainstream, financial barriers remain a significant limitation to widespread blockchain adoption in the food sector.
Lack of Standardization
The food industry operates across global markets, each with its own traceability regulations and compliance frameworks. This lack of standardization makes it difficult to establish a unified approach to blockchain adoption. For example, while the U.S. Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA 204) emphasizes record-keeping and digital traceability, other regions follow different protocols. Without harmonized global standards, interoperability between blockchain platforms remains limited, restricting data flow and consistency across international food supply chains.
Scalability
As food companies generate massive amounts of data daily, integrating blockchain with existing food traceability technology and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems becomes a complex task. High transaction volumes and network congestion can slow performance, making scalability a major concern. To overcome this, many developers are exploring hybrid blockchain models and off-chain data storage options that balance transparency with efficiency.
Despite these challenges, the future of blockchain food traceability looks promising. Continuous innovation, improved data automation, and collaboration across the supply chain are paving the way for more scalable, affordable, and standardized blockchain systems that will ultimately reshape how the world tracks and verifies food from farm to fork.
The Future of Blockchain Food Traceability
The next decade will redefine how food systems operate, with blockchain food traceability at the core of this transformation. As governments enforce stricter food safety regulations, including the FSMA 204 rule, the demand for transparent and verifiable supply chain data continues to grow. These regulations are accelerating the shift toward blockchain for food traceability, ensuring that food companies can validate every step of production, transport, and handling with undeniable accuracy.
The future will also see the rise of digital-first ecosystems where suppliers, retailers, regulators, and consumers share one unified source of truth. Blockchain food traceability will eliminate blind spots, reduce paperwork, and make recalls faster and more precise. As traceability expectations grow, blockchain will become the universal standard for food safety compliance, bridging the gap between trust and transparency across global markets.
Emerging technologies are further amplifying this shift. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) devices are merging with blockchain food traceability platforms to enable predictive insights, automated alerts, and data-driven decision-making. This convergence of blockchain in food industry technologies is setting the stage for more intelligent, interconnected, and efficient traceability systems, a direction where innovators like Folio3 FoodTech are playing a key role in helping businesses stay ahead.
How Folio3 FoodTech Supports Blockchain-Enabled Food Traceability
In a world where visibility and trust define success, Folio3 FoodTech helps businesses embrace blockchain food traceability with advanced digital solutions like its food traceability software, built for transparency, compliance, and efficiency. By combining smart automation with real-time insights, Folio3 enables food producers, processors, and distributors to meet modern food safety and regulatory demands confidently.
Core Features include:
- Blockchain-Powered Traceability Dashboards
- FSMA 204–Ready Food Safety Compliance Tools
- Real-Time Alerts for Contamination or Deviations
- Automated Risk Detection
- Audits & Risk Scoring
- Recall Optimization
- Integration with IoT Devices
- Batch-Level Quality Control
- Seamless ERP and QA System Integration
Folio3 FoodTech empowers the blockchain food supply chain with technology that enhances traceability, reduces risks, and strengthens consumer confidence. By aligning food traceability technology with automation and intelligent analytics, Folio3 is redefining how the blockchain in the food industry operates, building a safer, more transparent, and future-ready food ecosystem.
Conclusion
Blockchain food traceability is transforming how the food industry ensures safety, transparency, and accountability. By creating immutable records and real-time visibility across every stage of production and distribution, it minimizes risk and strengthens consumer trust. Choosing the right technology, system design, and monitoring practices is critical to unlocking the full potential of traceability.
As global regulations like FSMA 204 continue to raise standards, businesses that invest in blockchain in food industry solutions today will gain a competitive edge tomorrow. With partners like Folio3 FoodTech, companies can confidently adopt secure and intelligent systems that streamline compliance, enhance food safety, and create a more transparent global supply chain.
FAQs
How Is Blockchain Used in the Food Industry?
Blockchain is used in the food industry to record and verify every step of the supply chain, from farm to shelf. Each transaction is stored in a secure, tamper-proof ledger, enabling instant traceability of ingredients, batch histories, and logistics data. This helps companies improve food safety, reduce fraud, and build consumer trust.
Which Company Built a Blockchain-Based Food Traceability System?
Several companies have developed blockchain-based traceability systems. For example, IBM’s Food Trust network allows major brands and retailers to track products in real time. Similarly, Folio3 FoodTech helps businesses implement customized blockchain food traceability solutions integrated with ERP and IoT systems for end-to-end transparency.
What Is an Example of a Blockchain for Traceability?
A practical example is using blockchain to track seafood from fishing vessels to retail stores. Each stage, from catch documentation to cold-chain monitoring, is logged on the blockchain, ensuring authenticity, sustainability, and compliance with global food safety standards.
What Are the Benefits of Blockchain Food Traceability?
The main benefits include faster recalls, improved food safety, and increased consumer confidence. It also supports food safety compliance and reduces waste by improving visibility and coordination across suppliers, processors, and distributors.